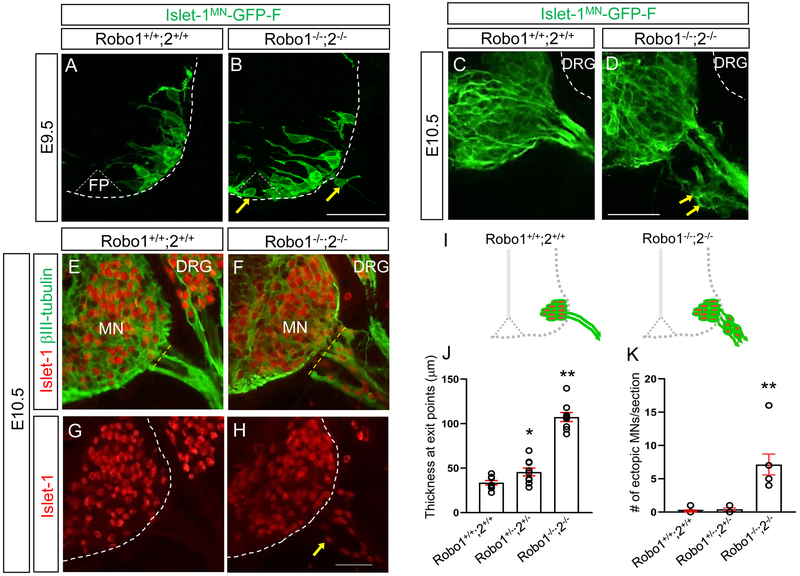
Figure 1. Islet-1+ Motor neurons migrate outside the spinal cord in Robo1/2 mutants.
(A, B) Spinal cord sections of Robo1+/+;2+/+::Islet-1MN-GFP-F and Robo1−/−;2−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F E9.5 embryos (n=4 embryos for each genotype) show that GFP+ motor neurons are positioned within their motor column in Robo1+/+;2+/+::Islet-1MN-GFP-F (A). Arrows in B show that GFP+ motor neurons migrate into the floor plate (FP) and emigrate out of the Robo1−/−;2−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F spinal cord. (C, D) Spinal cord sections of Robo1+/+;2+/+::Islet-1MN-GFP-F and Robo1−/−;2−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F E10.5 embryos (n=4 embryos for each genotype) show that GFP+ motor neurons are retained within their motor column in Robo1+/+;2+/+::Islet-1MN-GFP-F (C). Arrows in D show that GFP+ motor neurons emigrate out of the Robo1−/−;2−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F spinal cord. Note that DRG neurons (white dotted lines in C, D) are GFP-negative. (E-H) Islet-1 and βIII-tubulin labeling (E, F) or Islet-1 labeling (G, H) on E10.5 spinal cord sections of Robo1+/+;2+/+ and Robo1−/−;2−/− embryos showing that Islet-1+ motor neurons emigrate outside the Robo1−/−;2−/− spinal cord. (I) Schematics showing how motor neurons positioned in the E10.5 Robo1+/+;2+/+ and Robo1−/−;2−/− spinal cords. (J, K) Summary graphs show the thickness at motor exit points. The width of exit points was measured at the brachial level of the E10.5 spinal cords (dotted yellow lines in C and D) (H) and number of emigrating motor neurons (I) in Robo1+/+;2+/+, Robo1+/−;2+/− or Robo1−/−;2−/− embryos (n=7 embryos for each genotype). Both thickness and ectopic motor neurons are significantly increased in Robo mutants compared to their littermate controls. Scale bars: A, B, 50 μm; C, D, 50 μm; E-H, 50 μm. FP, floor plate, MN, motor neuron, DRG, dorsal root ganglion. *: P <0.05, **: P <0.001.