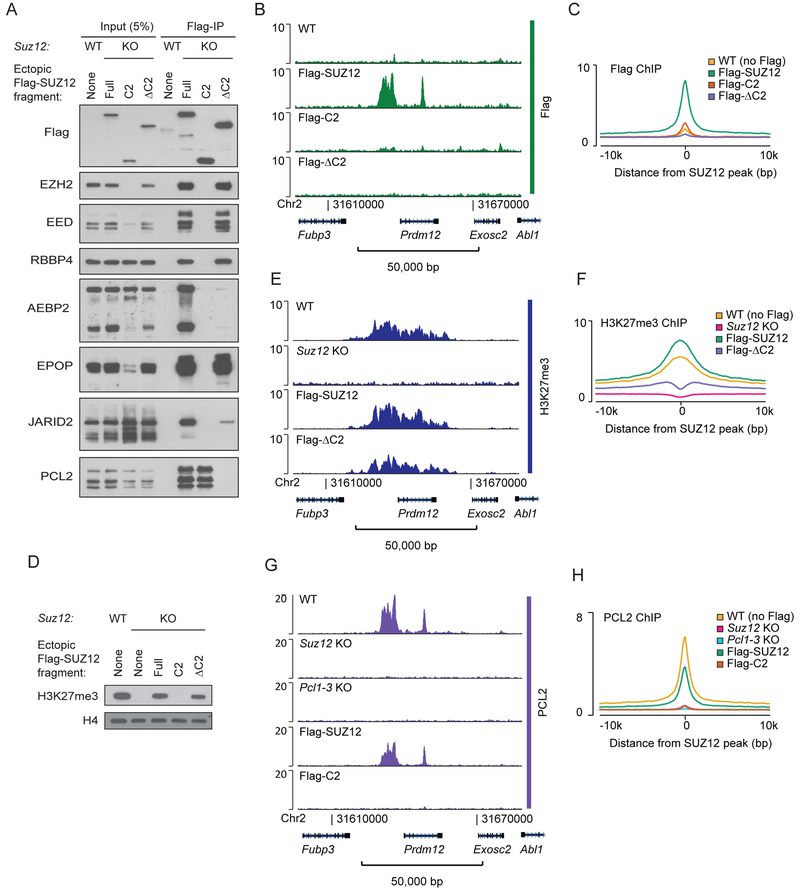
Figure 2: PCL2 binding to PRC2 target sites is dependent on SUZ12.
A) Western blot for PRC2 subunits of cell extracts (input) and anti-Flag immunoprecipitated material (Flag-IP) from the indicated cell lines (wildtype mESC (WT) or Suz12 KO mESC (KO) with ectopic expression of Flag-tagged SUZ12 fragments). Fragment boundaries are shown in Figure 1B.
B) Flag ChIP-seq signals (RPKM) from indicated cell lines expressing Flag-tagged SUZ12 constructs within a representative genomic region that includes the PRC2 target gene Prdm12. ChIP-seq signals in other representative genomic regions are shown in Supplementary Figure 2A.
C) Mean Flag ChIP-seq signals (RPKM) for WT mESC (no Flag) or Suz12 KO mESC with ectopic expression of Flag-tagged SUZ12 constructs in regions centered on 7,798 SUZ12 peak regions identified in WT mESCs.
D) Western blot for H3K27me3 (with H4 as a loading control) in extracts from the indicated cell lines.
E) H3K27me3 ChIP-seq (RPKM) signals within a representative genomic region from indicated cell lines. ChIP-seq signals in other representative genomic regions are shown in Supplementary Figure 2A.
F) Mean H3K27me3 ChIP-seq signals (RPKM) for WT mESC or Suz12 KO mESC with ectopic expression of Flag-tagged SUZ12 constructs in regions centered on 7,796 SUZ12 peak regions identified in WT mESCs.
G) PCL2 ChIP-seq signals (RPKM) from indicated cell lines within a representative genomic region that includes the PRC2 target gene Prdm12. ChIP-seq signal in other representative genomic regions are shown in Supplementary Figure 2B.
H) Mean PCL2 ChIP-seq signals (RPKM) from indicated cell lines in 7,796 SUZ12 peak regions identified in WT mESCs.