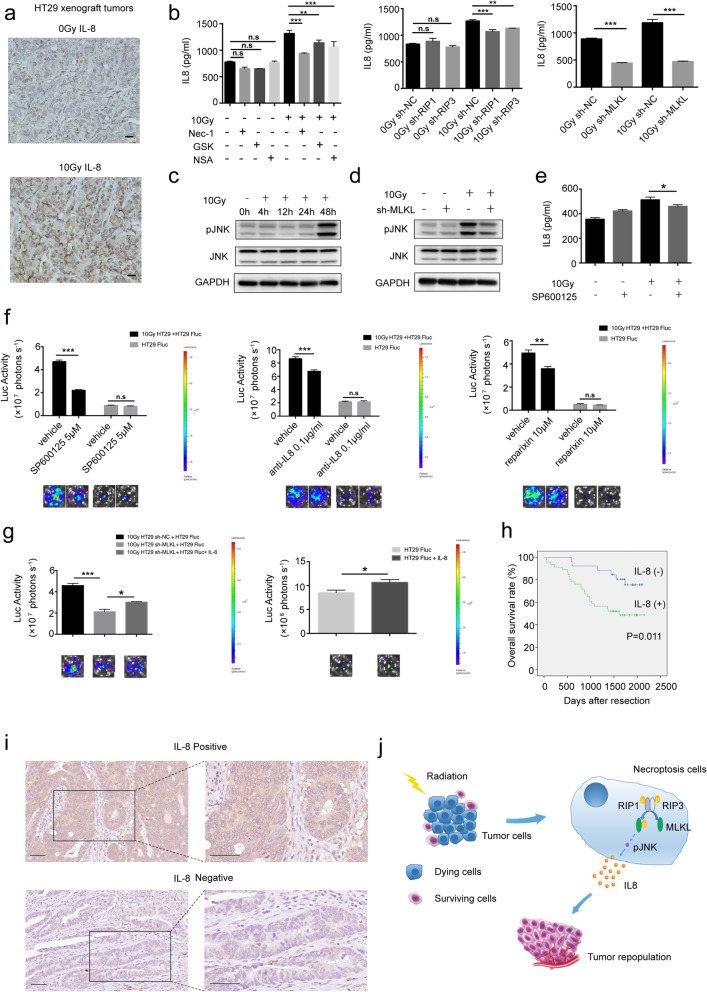
Fig. 6.
JNK/IL-8 (CXCL8): a novel downstream axis of necroptosis in tumor repopulation. a Immunohistochemical staining of IL-8 in the HT29 xenograft tumors for 48 h from 10 Gy-irradiated and no-irradiated nude mice. Scale bar: 20 μm. b Left panel, IL-8 concentrations were measured in the supernatants of HT29 cells (pretreated with RIP1 inhibitor (Nec-1), RIP3 inhibitor (GSK’872) or MLKL inhibitor (NSA) for 24 h) with no radiation or after 10Gy radiation for 48 h by chemiluminescent immunoassays. Right panel, IL-8 concentrations were measured in the supernatants of HT29 sh-NC, HT29 sh-RIP1, HT29 sh-RIP3 and HT29 sh-MLKL cells with or without 10 Gy radiation for 48 h, one-way ANOVA, n = 3. c Western blot showed the protein level of phosphorylated JNK1/2 and pan-JNK in HT29 cells after 10Gy radiation. d Western blot showed expression of phosphorylated JNK1/2 and pan-JNK in MLKL knockdown and vector-transfected HT29 cells for 48 h after 10 Gy radiation. e IL-8 concentrations were measured in the supernatants of HT29 cells (pretreated with JNK inhibitor (SP600125)) with no radiation or after 10 Gy radiation for 48 h by chemiluminescent immunoassays, one-way ANOVA, n = 3. f Effect of dying HT29 cells on growth of HT29 Fluc after treatment of JNK inhibitor (SP600125), anti-IL-8 antibody and reparixin (an inhibitor of IL-8 receptor CXCR1 and CXCR2), one-way ANOVA, n = 3. g Effects of recombinant Human IL-8 on dying HT29 sh-MLKL cells induced growth of HT29 Fluc (left panel) and on growth of HT29 Fluc alone (right panel), one-way ANOVA, n = 3. h The Kaplan–Meier survival analysis in 71 colorectal cancer patients. i Representative images of positive (upper panel) and negative (lower panel) IL-8 staining in human colorectal cancer tissues. Scale bar: 50 μm. j Schematic representation of the proposed mechanisms for necroptosis–mediated tumor cell repopulation. n.s = not significant, * < p 0.05, ** p < 0.005, *** p < 0.001