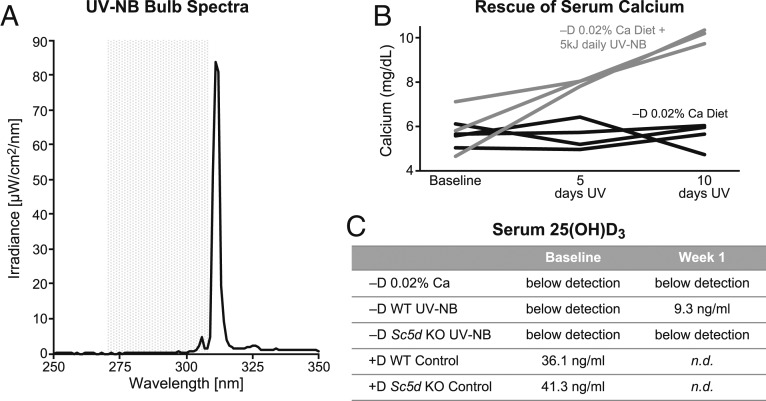
Fig. 3.
UV-NB is able to restore serum calcium in depleted mice through the generation of vitamin D. (A) The spectral output from UV-NB bulbs (300–325 nm, peak output 311–312 nm, black line) is generally beyond the wavelength required for robust generation of previtamin D3 in skin (shaded gray area) (20). (B) However, a moderate daily dose of UV-NB (gray lines) can rapidly restore serum calcium levels in calcium depleted vitamin D deficient mice (black lines) to normal levels. Mice bred under vitamin D deficient conditions were placed on a vitamin D deficient diet containing 0.02% calcium for 2 wk to achieve hypocalcemia. A subset of the mice was then exposed to UV-NB (black lines) for 5 consecutive days and their serum calcium measured; this was repeated the following week. UV-NB was able to partially rescue serum calcium by 5 d of exposure with full rescue occurring by 10 d of exposure. Each line represents the time course from 1 animal. (C) WT mice maintained on a vitamin D deficient diet and exposed to UV-NB show a rise above the detection threshold for serum 25(OH)D3 after only 5 daily doses of UV. By contrast, mice lacking the Sc5d enzyme are unable to raise their serum 25(OH)D3 by UV-NB. Each value represents a single sample pooled from 4 to 8 mice. n.d., not determined.