Figure 4.
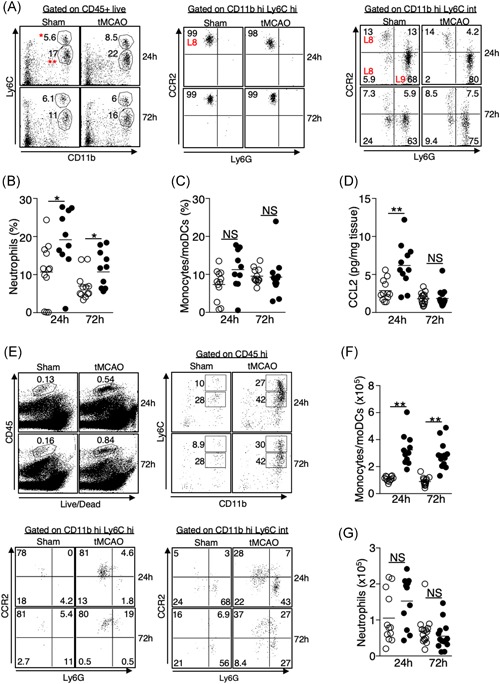
Increased infiltration of neutrophils but not monocytes to the lungs following ischemic stroke despite an elevation of CCL2. A‐C, Lung tissues were excised 24 and 72 hours following tMCAO or sham operation. Monocytes/moDCs and neutrophils in the lungs were analyzed by flow cytometry, defined by surface markers listed on Table 1. A, Representative plots showing the identification of monocytes/moDCs (L8) and neutrophils (L9) in the lungs. Monocytes/moDCs were defined as CD45+ Ly6C hi (*) CCR2 hi (middle) and Ly6C intermediate (**) CCR2+/− (right). Neutrophils were defined as CD45+ Ly6C intermediate (**) Ly6G+ (right). B‐C, Graphs showing percentage of neutrophils (B) and monocytes/moDCs (C) of individual animals 24 and 72 hours following tMCAO (filled circle) or sham operation (open circle). D, Lung tissues were homogenized 24 and 72 hours following tMCAO (filled circle) or sham operation (open circle), level of CCL2 was determined by multiplex bead array. E‐G, Brain tissues were excised 24 and 72 hours following tMCAO or sham operation, monocytes/moDCs and neutrophils in the brains were analyzed by flow cytometry. E, Representative plots showing the identification of monocytes/moDCs and neutrophils in the brains, which were defined as in (A). F,G, Graphs showing number of monocytes/moDCs (F) and neutrophils (G) of individual animals 24 and 72 hours following tMCAO (filled circle) or sham operation (open circle). Data shown are combined results from three independent experiments with n = 12 animals per group (sham 24 hours; tMCAO 24 hours; sham 72 hours; tMCAO 72 hours). *P < .05; **P < .01. moDC, monocyte‐derived dendritic cell; NS, not statistically different; tMCAO, transient middle cerebral artery occlusion
