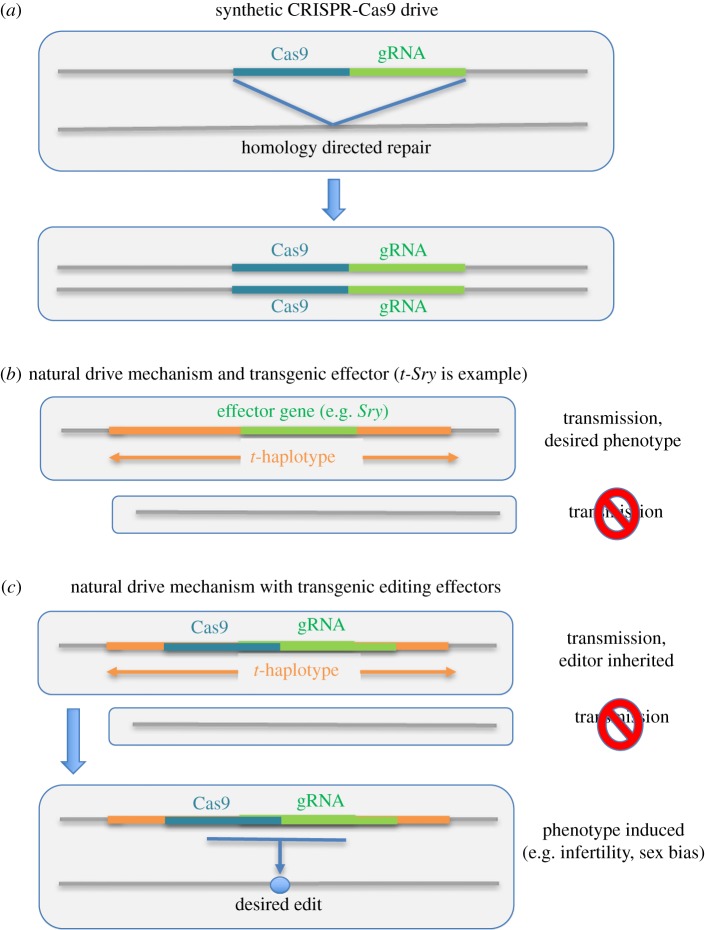
Figure 1.
Gene drive designs incorporating either synthetic or naturally occurring drive mechanisms. (a) A ‘standard’ CRISPR-based gene drive that relies on homing and HDR [43–46]. (b) The t-Sry approach in which spread depends on the naturally occurring t-haplotype system and a transgenic insertion of the masculinizing Sry gene [35,47]. Sperm that do not carry a t-haplotype are compromised in function and fertilization occurs with sperm carrying the t-haplotype (termed transmission ratio distortion). (c) A system that would spread through a natural drive mechanism (e.g. the t-haplotype) but incorporate CRISPR system effectors to produce genome edits and desired phenotypes. (Online version in colour.)