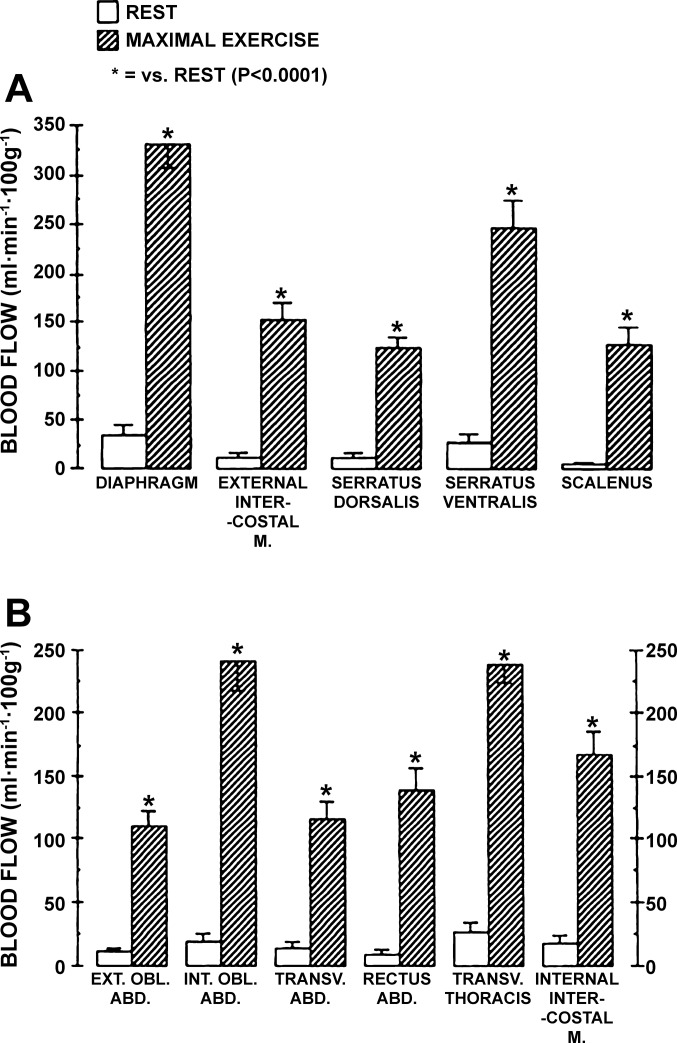
Fig. 3.
Blood flow to inspiratory (A) and expiratory (B) muscles of ponies at rest at rest and during maximal exercise. Data are from Manohar (51). EXT. OBL. ABD., external oblique abdominis; INT. OBL. ABD., internal oblique abdominis; TRANS. ABD., transverse abdominis; RECUTS ABD, rectus abdominis; TRANSV. THORACIS, transverse thoracis. Note, that without exception blood flow to the respiratory musculature during maximal exercise was significantly increased relative to resting conditions. Note that blood flow to the diaphragm exceeded 300 ml·min−1·100g−1; neither diaphragm flow or vascular conductance was increased further upon infusion of a vasodilator during maximal exercise.