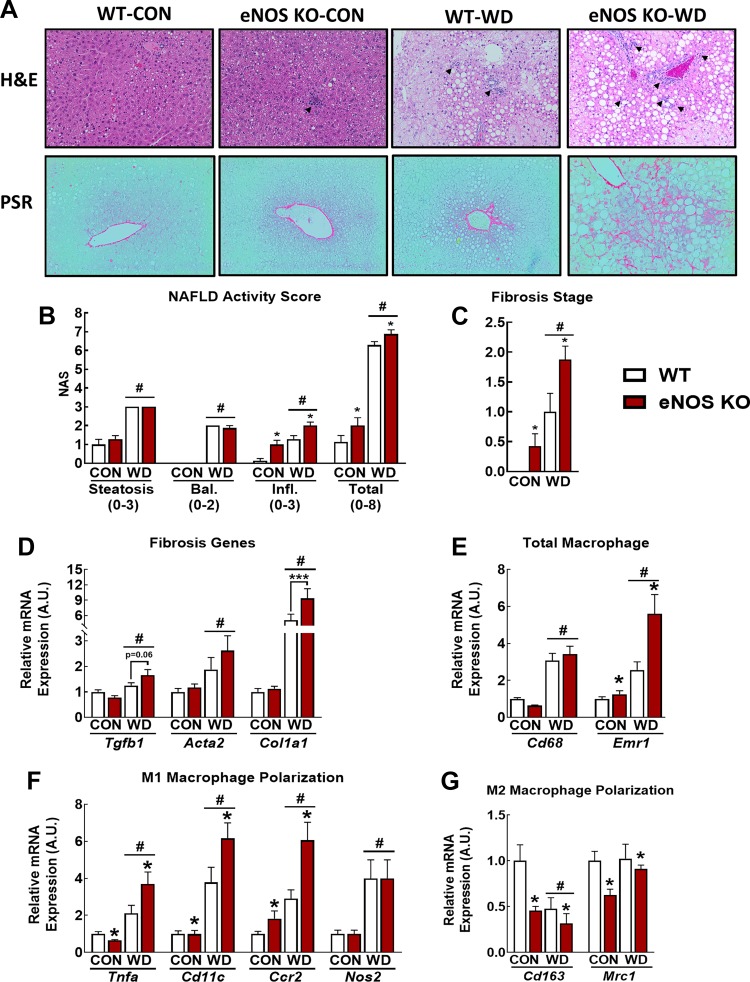
Fig. 3.
Endothelial NO synthase knockout (eNOS KO) increases hepatic fibrosis and inflammation. A: representative liver hematoxylin-eosin (H&E; top) and Picrosirius red (PSR; bottom) stains in control (CON)- and Western diet (WD)-fed wild-type (WT) and eNOS KO mice. Arrowheads indicate immune cell infiltrate. B: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity scores. C: fibrosis staging. D: qPCR markers of fibrosis. E: qPCR markers of total macrophage content. F: qPCR markers of proinflammatory M1 macrophage markers. G: qPCR markers of anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization; n = 7–8 mice/group. #P < 0.05 diet main effect; *P < 0.05 genotype main effect; ***P < 0.05 significant post hoc pairwise comparison indicated by bracket.