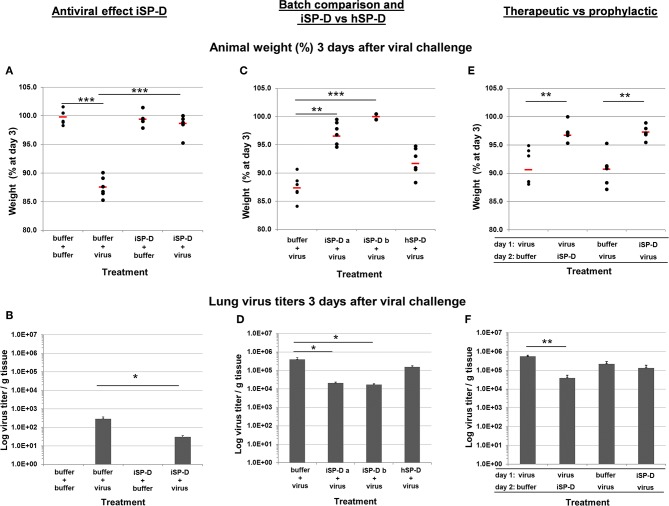
Figure 7.
Validation of iSP-D as antiviral agent against pandemic IAV infection in mice. The protective potential of iSP-D against pandemic IAV infection in vivo was assessed using the model as described in the materials and methods section and in Figure 6. Three different experiments were executed with 4 different conditions within each experiment; group size was n = 6 per condition. Administration of iSP-D or hSP-D and viral challenge (A/California/E9/09 (H1N1) strain, 1 × 103 TCID50) as described in the Materials and Methods. Three days after infection the average animal weights (% of weight at day 0) and average virus titers (log virus/g lung tissue) were determined for all experimental groups. Experiment I, (A) (animal weight) and (B) (virus titers): antiviral effect of iSP-D-delivery (25 μg/animal) immediately followed by viral challenge. Experiment II, (C) (animal weight) and (D) (virus titers): comparison of antiviral activity between 2 different batches of iSP-D and between iSP-D and hSP-D (5.0 μg/animal). Experiment III, (E) (animal weight) and (F) (virus titers): the antiviral effect of iSP-D (25 μg/animal) delivered 1 day after or 1 day before viral challenge. Statistical comparisons between experimental groups were made by Student's two-tailed paired t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005.