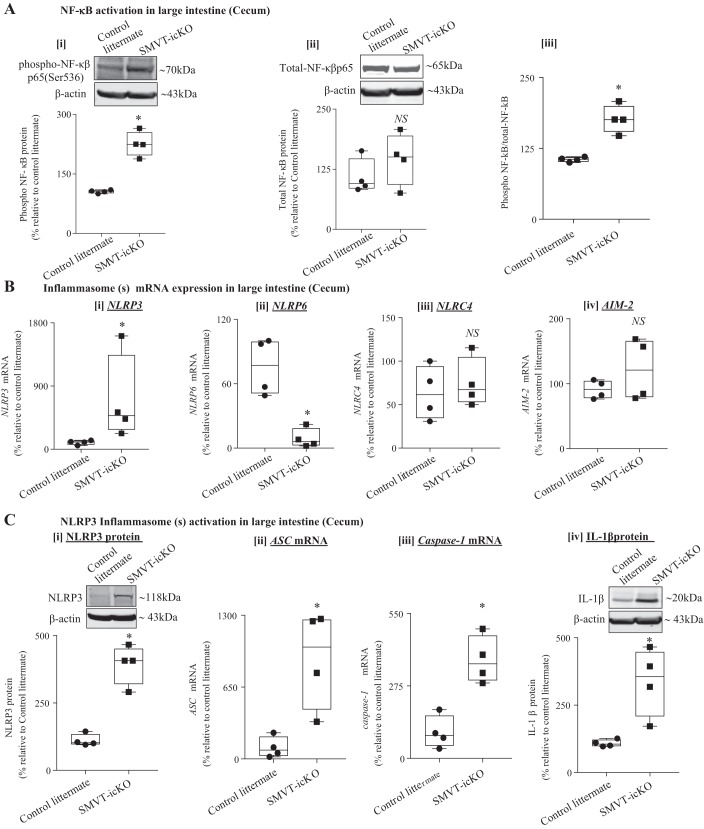
Fig. 4.
Involvement of NF-κβ signaling pathway and inflammasome(s) in the intestine of sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT)-inducible, conditional knockout (icKO) mice. A: representative Western blotting bands and the bar diagrams show the relative phospho-NF-κB (i), total-NF-κB (ii), and ratio of phospho- and total-NF-κB (iii) protein expression in cecum of SMVT-icKO mice and their control littermates. B: level of mRNA expression of different inflammasomes [nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin 3 domain (NLRP3) (i), nucleotide-binding domain–like receptor family pyrin domain containing 6 (NLRP6) (ii), nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat family caspase activation and recruitment domain containing 4 (NLRC4) (iii), and absent in melanoma (AIM)-2 (iv)] in the cecum of SMVT-icKO mice and their control littermates. C: activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in the cecum of SMVT-icKO mice. Level of expression of NLRP3 protein (i), level of mRNA expression of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a COOH-terminal caspase-recruitment domain (ASC) (ii), level of mRNA expression of caspase-1 (iii), and level of expression of mature IL-1β protein in cecum of SMVT-icKO mice and their control littermates (iv). mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR, and data were normalized relative to GAPDH. Protein expression levels were determined by Western blot, and data were normalized to β-actin. All RT-qPCR and Western blot data are presented as box and dot-whisker plots from four separate sets of mice and statistical significance (*P < 0.05) are calculated with Mann-Whitney test. NS, not significant.