FIGURE 5.
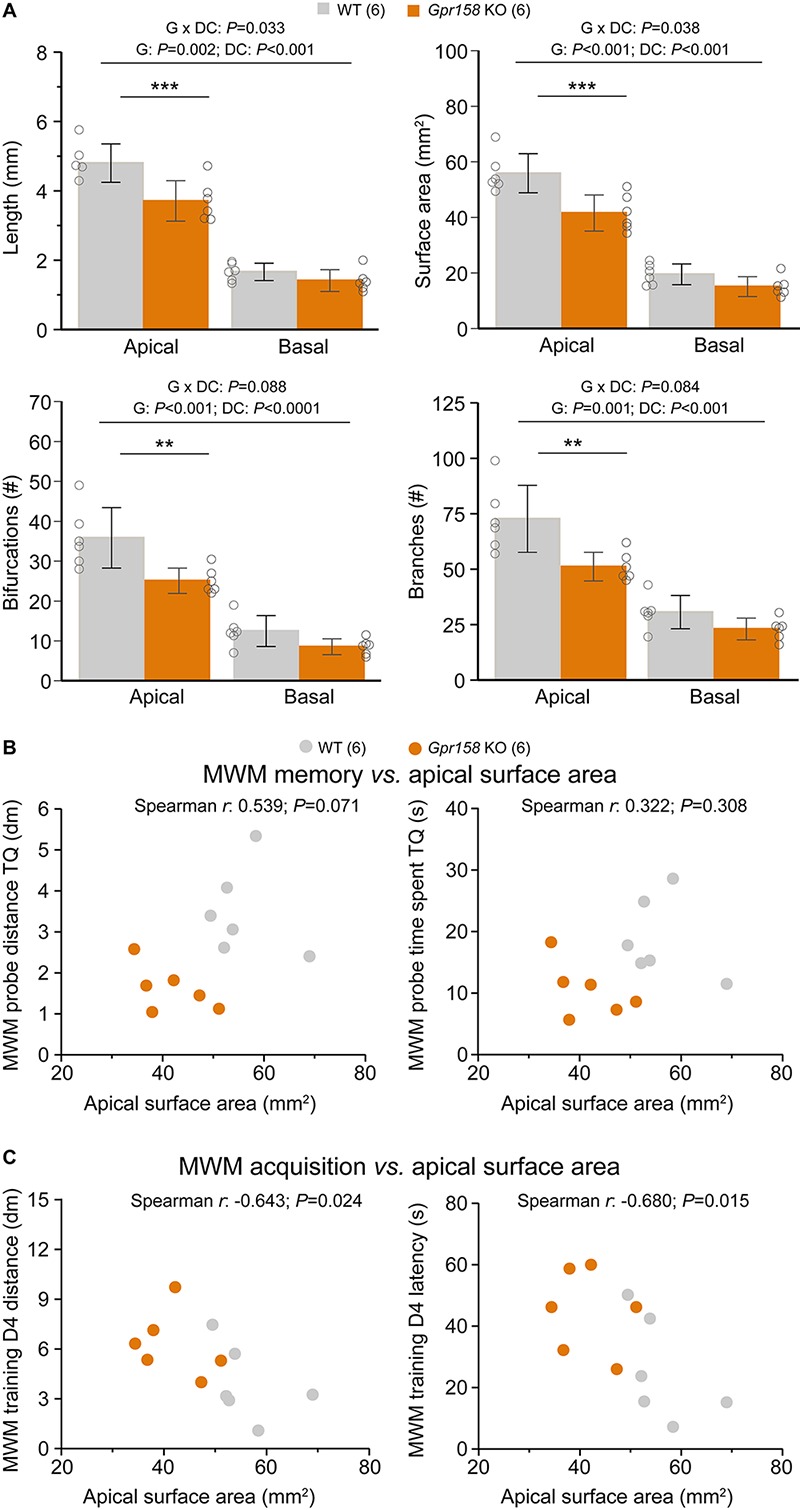
Reduced dendritic architecture negatively impacts learning during MWM training. (A) Cell morphology from all the electrophysiological data sets described were averaged to generate an overview of hippocampal dendritic architecture per animal (WT n = 6 animals, 18 cells averaged, KO n = 6 animals, 17 cells averaged). Apical but not basal hippocampal dendritic length, surface area, bifurcations and branches were significantly reduced in Gpr158 KO animals. (B) Apical surface area did not (significantly) correlate with either the distance covered (P = 0.071) or the time spent (P = 0.308) in the target quadrant (TQ) during the MWM probe test assessing long-term memory. (C) During acquisition of the MWM task, the apical surface area did significantly and negatively correlate with both the distance covered to reach the platform (P = 0.024) and the latency (P = 0.015) reaching the platform on the last training day (D4). Data are presented as mean ± SD with individual data points indicated. Asterisks indicate significant differences between WT and KO assessed by Student’s t-test (Supplementary Table 5), ∗∗P ≤ 0.010; ∗∗∗P ≤ 0.001.
