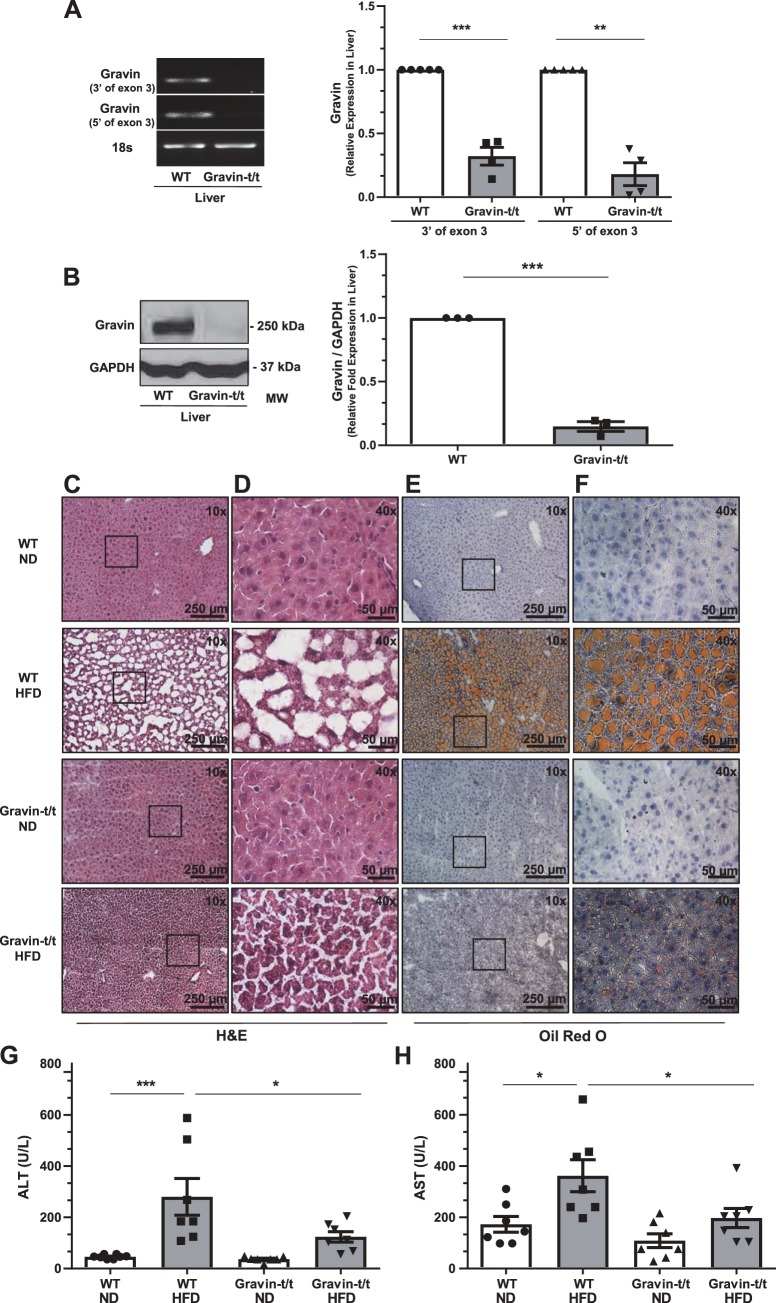
Fig. 5.
Gravin-t/t mice show reduced hepatic fat accumulation in response to high-fat diet (HFD). Gravin mRNA expression in the liver was quantified by reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR from wild-type (WT) and gravin-t/t mice (A). The liver from gravin-t/t mice showed significantly decreased gravin mRNA expression compared with WT mice. Results are presented as mean ± SE. n = 4; ***P = 0.0006 and **P = 0.0063. Gravin protein expression was measured in the liver by Western blot from WT and gravin-t/t mice, where the gravin antibody recognized the monomeric (250 kDa) forms of the gravin protein (B). The liver from gravin-t/t mice showed significantly decreased gravin protein expression compared with WT mice. Results are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3; ***P < 0.001). Dissected livers (C–F) were isolated from gravin-t/t and WT mice, sectioned, frozen, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E; C and D) and Oil Red O (counterstained with hematoxylin; E and F) following 16 wk of treatment with either normal diet (ND) or HFD. Images were measured using brightfield Nikon microscopy at ×10 (C and E) and ×40 (D and F). Boxed areas shown in C and E are shown in higher magnification in D and F, respectively. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT; G) and serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST; H) were both decreased in gravin-t/t HFD-fed mice compared with WT HFD-fed mice, showing greater liver damage and more lipid accumulation in gravin-t/t HFD-fed mice compared with WT HFD-fed mice. Results are presented as mean ± SE; n = 7 (G and H); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Comparisons between two groups were determined by an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, and comparisons between multiple groups were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test.