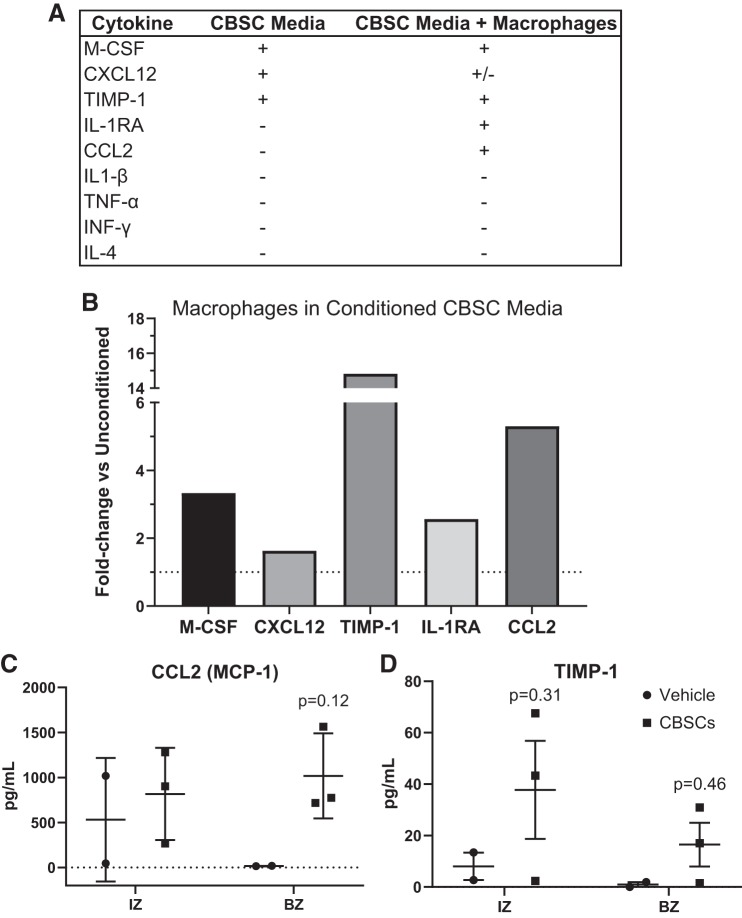
Fig. 3.
CBSCs secrete soluble signals that can alter immune cell recruitment. Soluble factors in media exposed to CBSCs for 48 h were analyzed by fluorescent antibody-based dot blot and densitometry, shown in a representative list (A). Densitometry values were obtained for macrophages exposed to conditioned or unconditioned CBSC media for 24 h, and the average values for each marker in the conditioned media group was divided by the average values for the unconditioned media group to obtain the fold change between groups (B). Dotted line represents y = 1. Quantitative proteomics on snap-frozen heart tissue 7 days after AMI was performed (C and D). Error bars represent ± SD. n = 3 for CBSC and n = 2 for vehicle groups. P values reflect the results of a 2-way ANOVA interactions between CBSC and vehicle groups. Multiple comparisons were corrected for by using Sidak’s method for multiple comparisons. AMI, acute myocardial infarction; BZ, border zone; CBSC, cortical bone stem cell; CCL2, chemokine C-C motif ligand 2; CXCL-12, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; IL-1RA, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; IZ, infarct zone; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; M-CSF, macrophage-colony stimulating factor; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase metallopeptidase inhibitor 1.