Fig. 7.
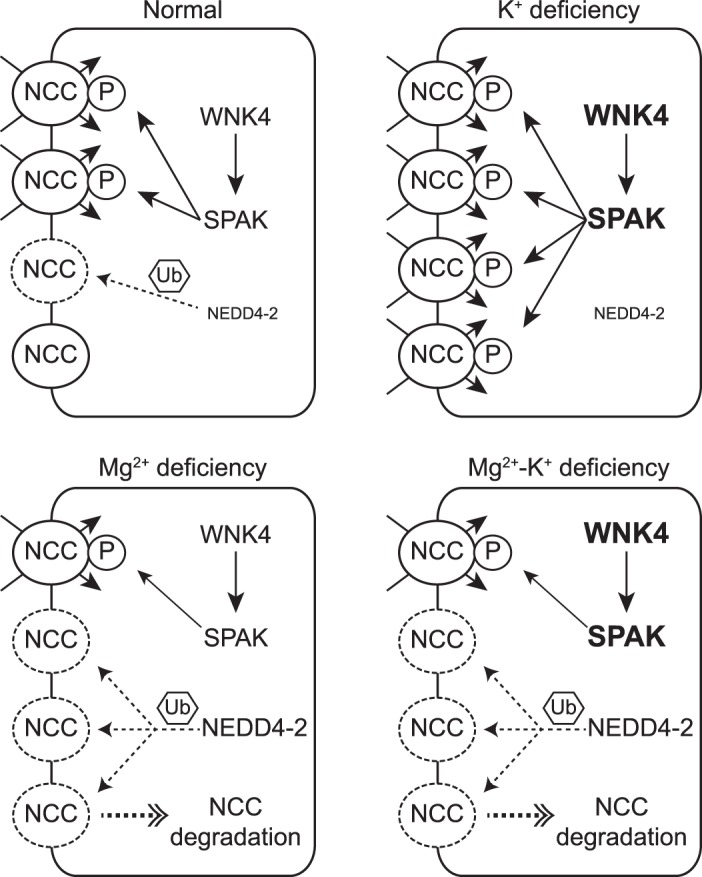
Model of the effect of dietary Mg2+ deficiency on total Na+-Cl− cotransporter (tNCC) in the setting of hypokalemia. With-no-lysine (K) kinase-4 (WNK4)-STE20/SPS-1-related proline/alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) is the major signaling pathway to activate NCC, whereas E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase neuronal precursor cell developmentally downregulated 4-2 (NEDD4-2) plays a key role in the catabolism of NCC. It is well established that dietary K+ deficiency activates NCC by phosphorylation through the WNK4-SPAK signaling pathway along the distal convoluted tubule. During K+ deficiency, NEDD4-2 spares NCC and mainly targets the epithelial Na+ channel. Dietary Mg2+ deficiency downregulates NCC, possibly through NEDD4-2. In the state of both Mg2+ and K+ deficiency, downregulation of NCC abundance, due to Mg2+ deficiency, prevents K+ deficiency-mediated NCC activation by phosphorylation through WNK4-SPAK. The effect of Mg2+ deficiency on NCC is independent of WNK4 and SPAK.
