Fig. 1.
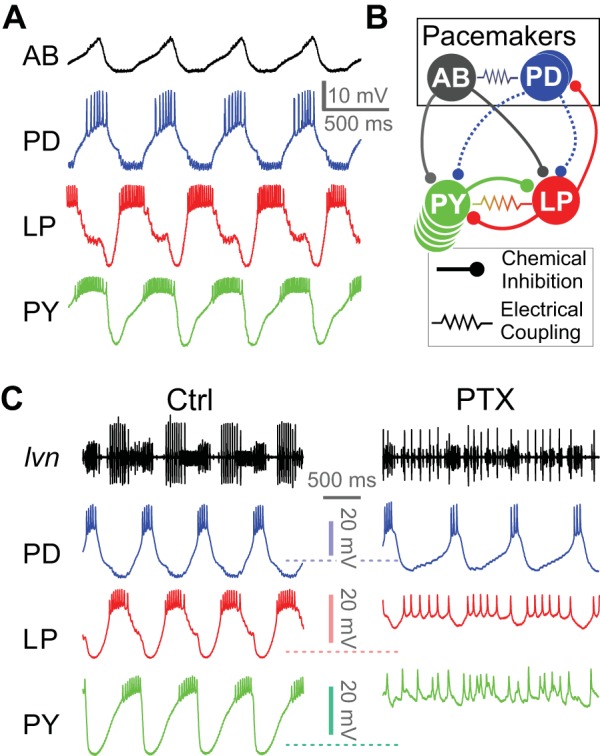
Jonah crab pyloric circuit activity, connectivity and response to pharmacological block of glutamatergic synapses. A: intracellular recordings of the anterior burster (AB), pyloric dilator (PD), lateral pyloric (LP), and pyloric constrictor (PY) neurons during ongoing pyloric activity. B: schematic diagram of the pyloric circuit, consisting of the AB and PD pacemaker ensemble neurons and the follower LP and PY neurons. Putative cholinergic synapses from the PD neuron are shown as dashed curves. C: simultaneous extracellular recording from the lateral ventricular nerve (lvn; containing the axons of PD, LP, and PY neurons) and intracellular recordings of the PD, LP, and PY neurons in control saline (Ctrl) and in the presence of 10−5 M picrotoxin (PTX), which blocks glutamatergic transmission in the stomatogastric ganglion (STG). Rhythmic activity in PD continues in PTX, but the LP-induced inhibitory postsynaptic potentials disappear. Residual rhythmicity remains in the LP and PY neurons.
