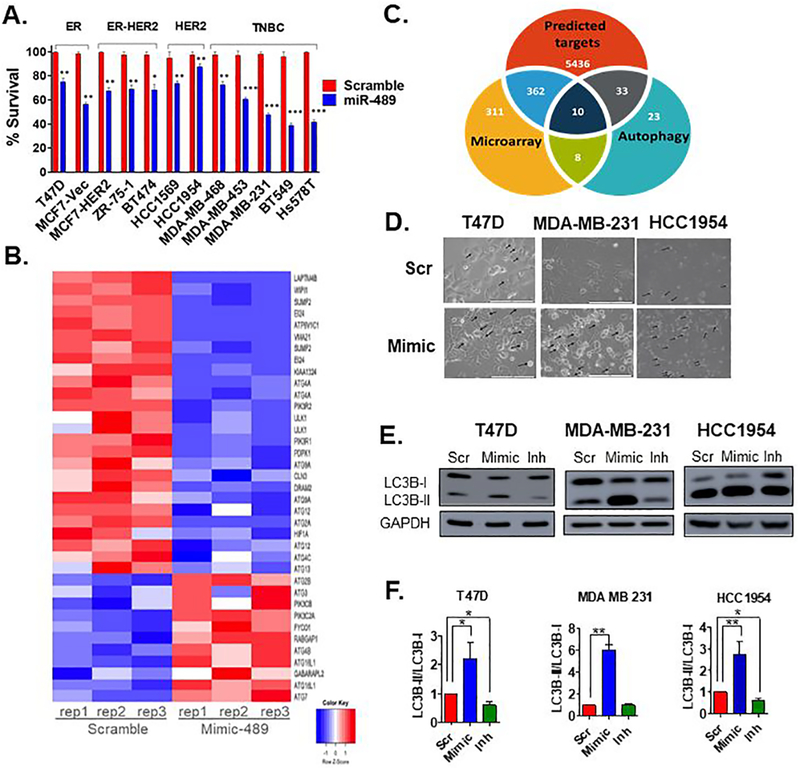
Fig. 1. miR-489 inhibits breast cancer cell growth and modulates multiple genes involved in autophagy.
A. MTT based cell proliferation/viability assay measuring viability of indicated breast cancer cell lines at 72hrs post transfection with 28nM scramble control miRNA (Scr) and miR-489 mimic (Mimic). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Data are representative of three independent experiments. B. Heatmap analysis of microarray data for the genes associated with autophagy. Genes were selected based on their differential expression between the scr transfected cells and mimic transfected cells. Red and blue indicate high and low gene expression, respectively. C. Hypergeometric analysis was performed using microarray data and putative targets identified using microRNA target-predicting software. D. Bright-field microscopy images of Scr or Mimic transfected cells. Arrow indicates intracellular endosomal, possibly vacuolar structures. Data are representative of three independent experiments. E. Indicated breast cancer cell lines were transfected with scr, mimic or miR-489 inhibitor (Inh). Protein was collected 72hrs post transfection and subject to western blot analysis of autophagy markers. GAPDH was used as a loading control. F. Quantification of LC3B-I and LC3B-II ratio.