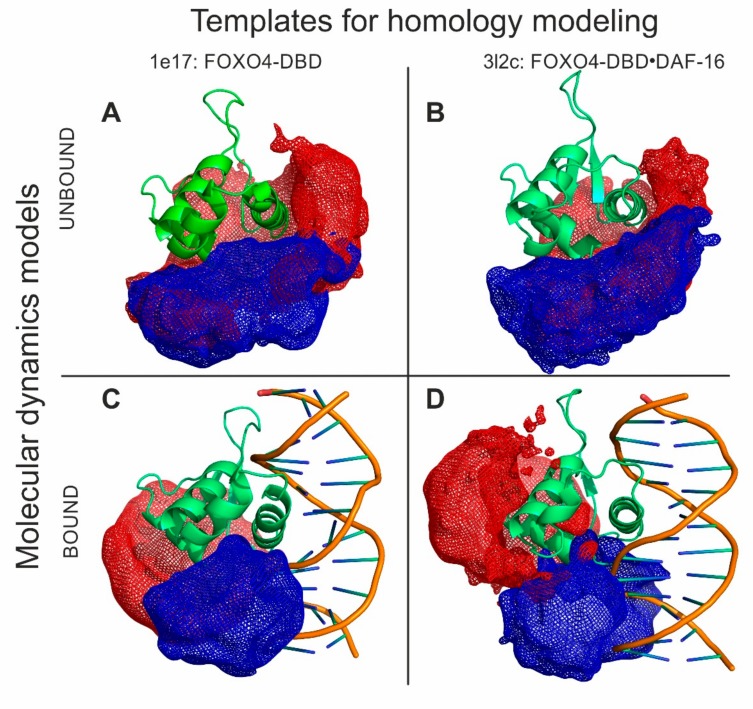
Figure 5.
Structural proteomics could effectively guide model-building operations to produce very high-quality 3D models. Models of FOXO4-DBD and FOXO4-DBD•DBE were obtained by combining homology modelling with experimental constraints and molecular dynamics simulations. These models incorporated extensive information from protein-DNA cross-links, quantitative protein-protein cross-links, and hydrogen-deuterium exchange. The green structures show representative models for unbound (A,B) and bound (C,D) forms based on corresponding 1E17 (A,C) or 3L2C (B,D) high-resolution templates. Mesh areas in blue and red colors represent spaces occupied by all the models in the ensembles, which provided a measure of the flexibility of the N- and C- terminal regions (see also Figures S10–S32 and Tables S1 and S2 of Supplementary Materials).