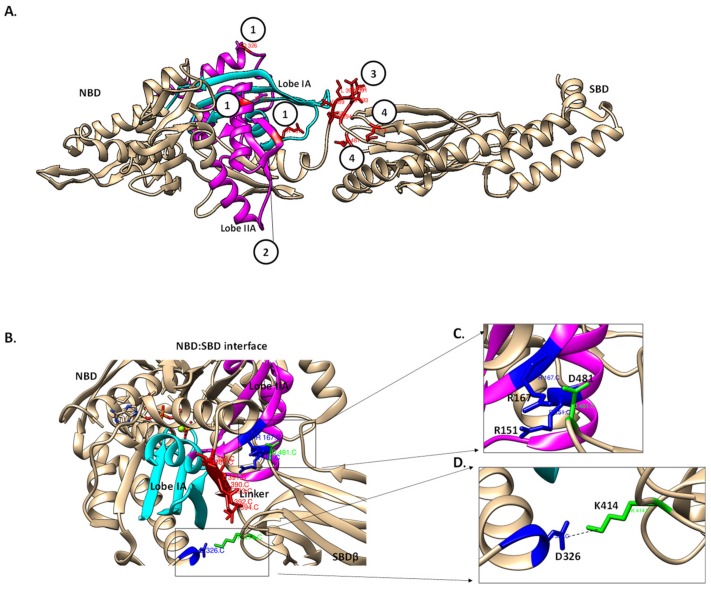
Figure 7.
The potential Hsp70 allosteric hotspots for drug targeting. The model of Hsp70 potential drug target sites that are modulated by the linker. (A) Hsp70 major allosteric hotspots located are shown in red. (1) NBD residues involved in the formation of the NBD–SBD interface (R151, R167 and D326 based on DnaK numbering); (2) the linker binding cleft between lobe IA (magenta) and IIA (cyan) form the hydrophobic linker binding cleft which is crucial for linker docking in the ATP state; (3) linker residues such as V389 and D393, hence, are also crucial for the NBD–SBD interface formation and (4) SBD residues, K414 and D481 (based on DnaK) that are crucial in the formation of the NBD–SBD interface [51]. (B) The NBD–SBD interface is shown with the allosteric hotspots in the NBD (blue) and SBD (green), respectively. The linker docked onto the linker binding cleft facilitates the formation of the NBD–SBD interface. NBD residues R167, R151 (blue) and the SBD (green) residue D481 form a part of NBD–SBD [51] (C), while NBD residues, D326 and K414 interact through hydrogen bonding thus stabilizing the interface (D) [51].