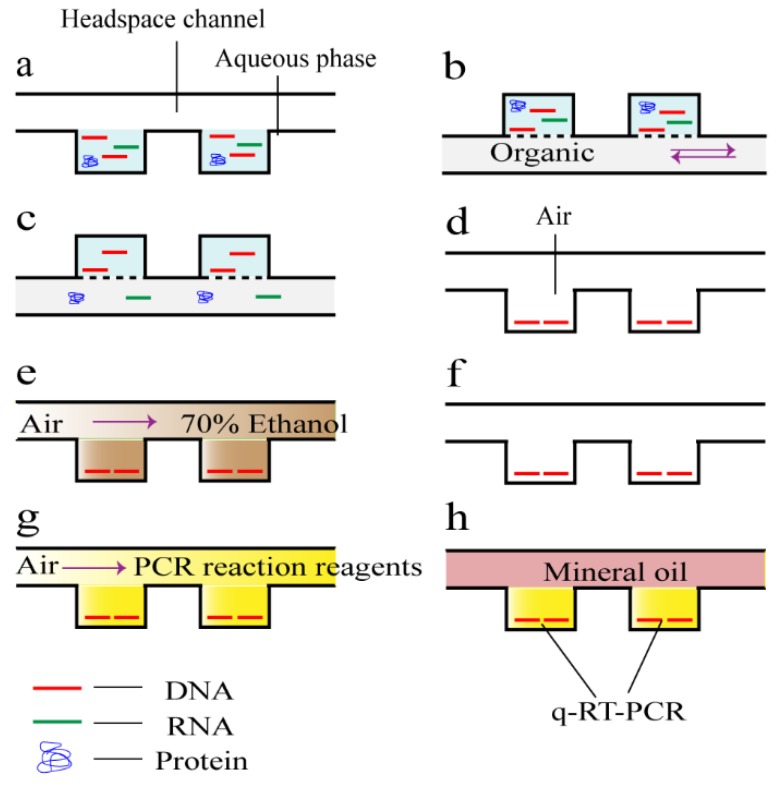
Figure 3.
Schematic of the DNA purification process in a liquid-phase DNA isolation chip described by Zhang et al. [51]. (a) An aqueous phase containing DNA, RNA, and protein was loaded in the microwells. (b) An organic phase with pH 8.0 was introduced into the headspace channel with continuous forward and reverse flow. The chip was inverted for nucleic acid purification in this step as the organic phase has greater density than the aqueous phase. (c) Protein and RNA were transferred from the aqueous phase into the organic phase, while DNA remained in the aqueous phase. (d) The organic phase was expelled from the headspace channel and evaporated under vacuum while purified DNA in the microwell was concurrently dried (e, f). Residual organic phase was further decontaminated by repetitive washing and vacuum evaporating with 70% ethanol. (g) q-RT-PCR reaction mixture was loaded into the microwells. (h) Microwells were covered with mineral oil followed by on-chip q-RT-PCR amplification.