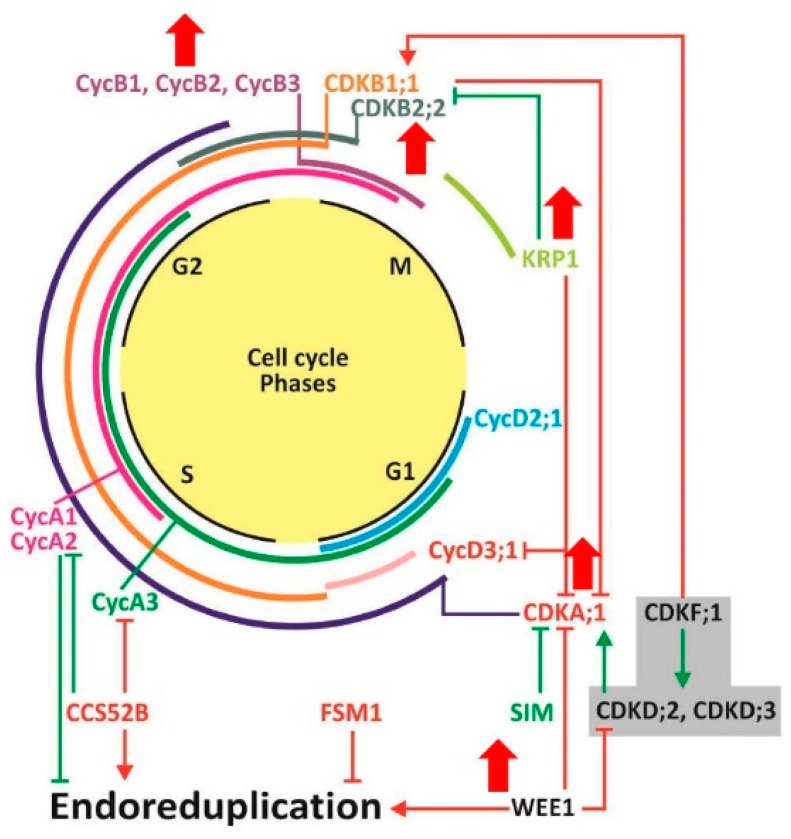
Figure 9.
A model showing the polyamine-mediated changes in transcript levels of genes involved in cell cycle progression and endoreduplication during tomato fruit development. In eukaryotes, cell cycle is mainly comprised of interphase and mitosis (M phase). Interphase is further divided into three phases: i) G1 (Gap 1) during which cell increases in size and becomes ready for DNA synthesis; ii) S (Synthesis) where DNA replication occurs; and iii) G2 (Gap 2) during which cell either continues to grow until ready for mitosis or enter into DNA amplification phase, called endoreduplication [58,59]. Expression levels of cyclins or CDKs during different phases of cell cycle progress are indicated in colors. CDK-activating kinases are highlighted in gray box. Transcript levels of genes enhanced by higher polyamines (Spd/Spm) are indicated with upward-facing thick red arrows. Abbreviations: G—Gap phase; M—Mitosis phase; S—Synthesis phase; Cyc—Cyclins; CDKs—Cyclin dependent kinases; KRPs—Kip-related proteins.