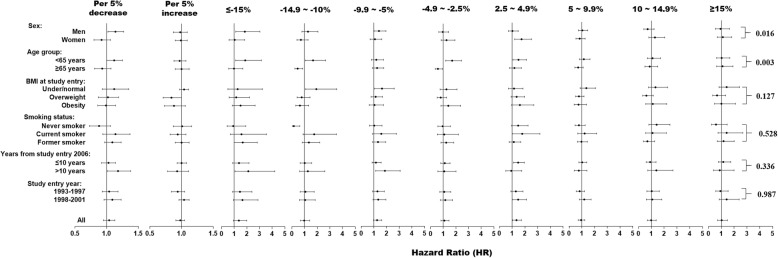
Fig. 4.
Associations between percentage change in BMI from study enrolment (1993–2001) to follow-up (2006) and the risk of cancer-related mortality. The reference value (HR = 1) was set at percentage change between − 2.5 and 2.5%. HRs were estimated by cox proportional hazard model adjusted of sex, age, race, education level, family annual income, marital status, physical activity level, family history of cancer in their first-degree relatives, smoking status, screening arm, history of chronic diseases (i.e., hypertension, heart attack, stroke, emphysema, diabetes, arthritis, and osteoporosis), and BMI value at study entry (continuous)