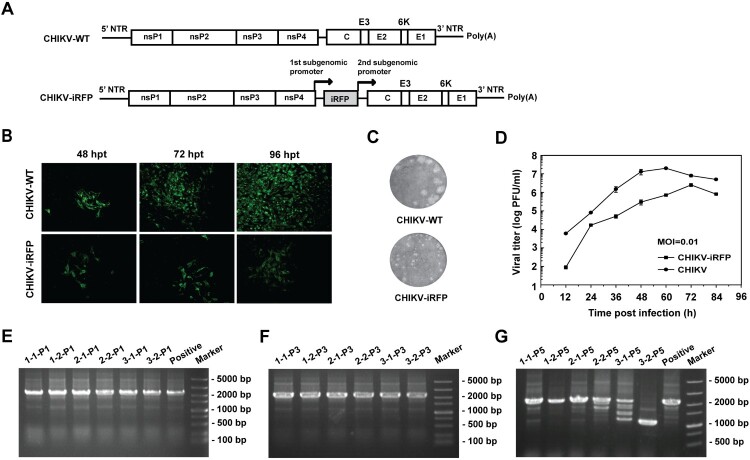
Figure 1.
Construction and characterization of CHIKV-iRFP. (A) Schematic representation of WT CHIKV and CHIKV-iRFP reporter viruses. An infectious cDNA clone of CHIKV was used as a backbone for the construction of CHIKV reporter virus. The expression of iRFP reporter gene was driven by a duplicate subgenomic (SG) promoter. Arrows represent SG promoters. (B) IFA analysis of viral E2 expression in BHK-21 cells transfected with in vitro transcribed genome-length RNAs of WT CHIKV and CHIKV-iRFP. (C) Plaque morphology of WT CHIKV and CHIKV-iRFP reporter viruses in BHK-21 cells. (D) Comparison of the growth kinetics of WT CHIKV and CHIKV-iRFP reporter viruses. The growth of WT CHIKV and CHIKV-iRFP were compared at an MOI of 0.01 in BHK-21 cells. Three independent experiments were performed in duplicate, and the representative data were presented. Error bars represent standard deviations. (E–G) Detection of the iRFP reporter gene during viral passage. Viral RNAs were extracted from the cells of P0 to P5 passage, respectively. RT-PCR was performed with a primer pair locating between the region of nsP4 and C. The numbers of time points-samples-passage were denoted on the top of each lane.