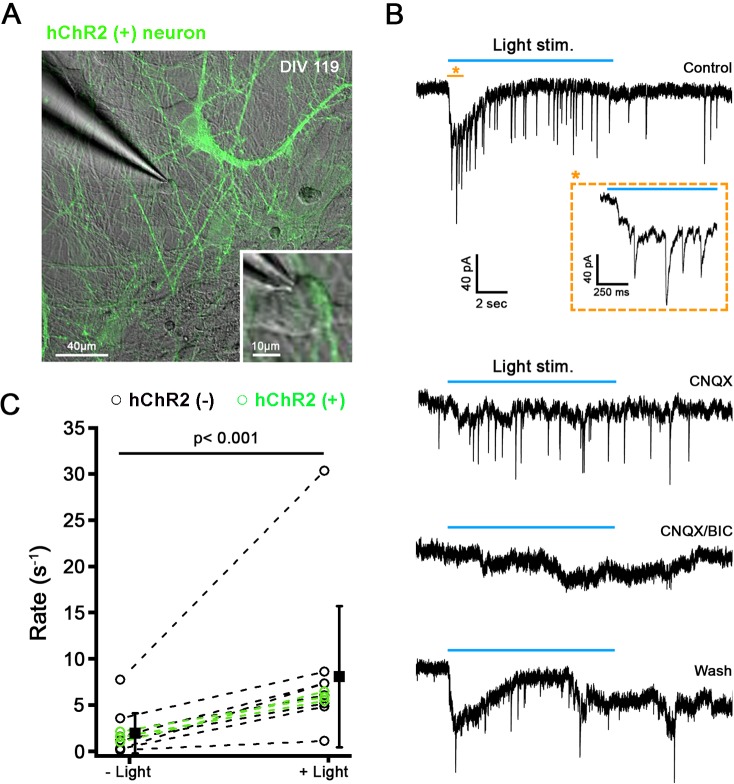
Fig 16. Light stimulation of hChR2-hNP-derived neurons triggers postsynaptic events in ChR2- and ChR2+ neurons.
(A) Confocal image showing ChR2+ neurons (green) in co-culture with ChR2- neurons after 119 days in vitro. (B) Example of a voltage clamp recording from a ChR2- neurons in co-culture with ChR2+ neurons; same cell as shown to be recorded in A. In response to light stimulation (blue bar), a slow inward current and synaptic events were triggered in control conditions (top trace). Inset shows an extended time scale of the recording time. The postsynaptic responses were blocked by the presence of CNQX and bicuculine suggesting that they were due to light stimulation of presynaptic hChR2+ neurons. (C) Synaptic rate before and during light stimulation plotted for individual recordings of ChR2- neurons (n = 8) and ChR2+ neurons (n = 3). Solid black squares represent mean of combined ChR2- and ChR2+ neurons, respectively (mean ± SD). For ChR2- neurons, the synaptic rate increased about 4-fold during light stimulation, from 2.2 ± 2.4 to 8.9 ± 8.4 events/s (n = 8; p < 0.05, paired t-test).