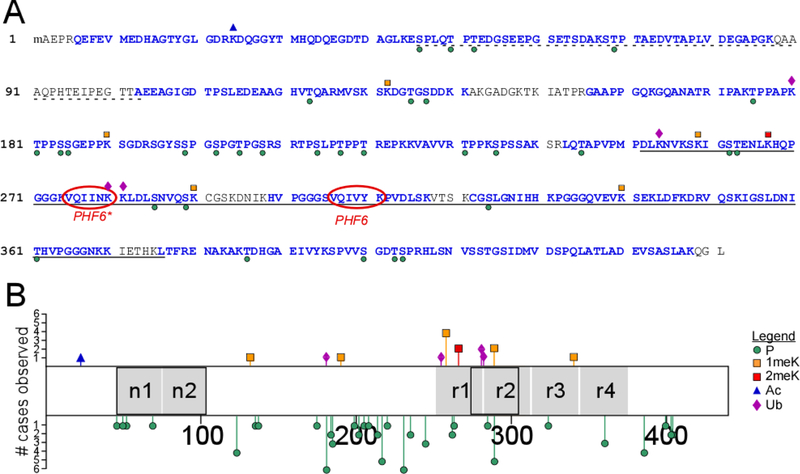
Fig. 1.
Post-translational modification sites on soluble tau proteins isolated from cognitively normal elderly identified by LC-MS/MS (cases 5, 6, 8–11, Table 1). (A) Identified tryptic peptides in the context of the human 2N4R isoform (NCBI accession number NP_005901), where the dotted underline depicts alternatively spliced projection domain segments n1 and n2, the solid underline identifies the MTBR (as defined in [53]), and PHF6/PHF6* mark the hexapeptide segments involved in filament nucleation [54]. Blue font color depicts sequence coverage. Phosphorylation (P) and ubiquitylation (Ub) sites are marked by green circles and purple diamonds, respectively, whereas mono- (1meK) and di-methylation (2meK) sites are indicated by orange and red squares, respectively. (B) Tau methylation and phosphorylation site distribution map (2N4R tau), showing location of modification sites relative to projection domain segments n1 and n2 and MTBR repeats r1 – r4 (black boxes depict alternatively spliced segments). The length of each bar corresponds to the number of cases in which the modification was found (# cases observed).