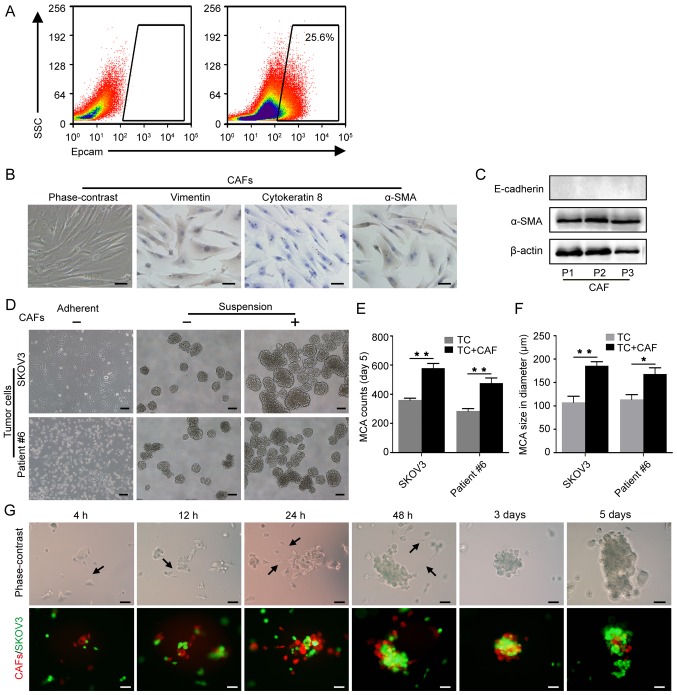
Figure 3.
CAFs promote MCA formation. (A) EpCAM+ tumor cells were isolated from the ascitic fluid by flow cytometric cell sorting. (B) Identification of primary CAFs isolated from omentum with metastasis; spindle-shaped, vimentin-positive, cytokeratin 8-negative and α-SMA-positive characterization. Scale bars, 50 µm. (C) Western blot analysis of α-SMA expression in primary CAFs; passage 1-3. (D) Representative images of MCA formation assays. SKOV3 and primary tumor cells isolated from patient #6 were cultured alone or co-cultured with CAFs in suspension. Scale bars, 100 µm. (E) Histograms show the MCA counts from the MCA formation assays. (F) Histograms show MCA size in the MCA formation assays. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (G) The dynamic process of tumor cell-CAF MCA formation. CAFs and SKOV3 cells were labeled with FM4-64 (red) and GFP (green), respectively. Black arrows indicate the filopodia of CAFs. Scale bars, 50 µm. CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; MCA, multicellular aggregate; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin.