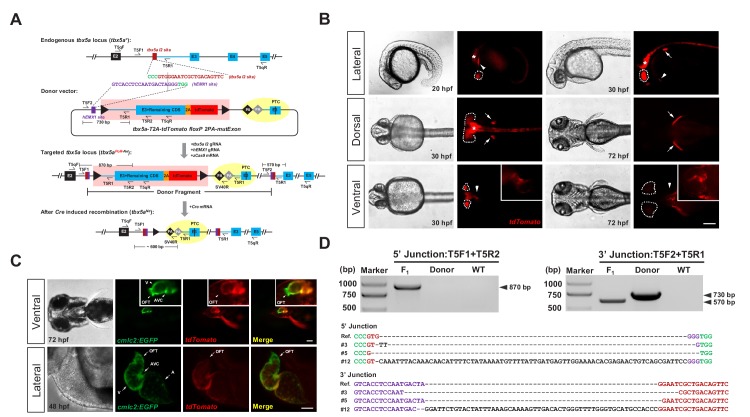
Figure 1. Generation of CKO coupled with gene labeling dual-function alleles through targeted insertion in zebrafish at the tbx5a locus.
(A) Schematic diagram of the KI strategy based on the dual-cassette PoNe donor tbx5a-T2A-tdTomato floxP 2PA-mutExon (the tbx5a PoR-Ne donor), consisting of a Po-cassette and a Ne-cassette (highlighted by pink and yellow shadows, respectively). The target sequences of hEMX1 and tbx5a are shown in purple and brown, respectively, and the PAMs are in shown green. Black triangles represent loxP. Black and gray diamonds indicate polyadenylation (PA) signals. The black bar in the third exon (E3) indicates the in-frame premature termination codon (PTC). Primers T5qF and T5qR are used for qRT-PCR in Figure 2—figure supplement 1E and F. (B) Images of F1 larvae from an outcross of a tbx5a PoR-Ne donor knockin founder (#12), showing tdTomato expression in the pectoral fins (white arrows), heart (white arrowheads), eyes (white dotted circle) and nervous system (white asterisk). Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Images of F1 progeny from Tg(cmlc2:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish crossed with the tbx5a KI founder (#12), showing an antero-posterior gradient of tbx5a expression in the ventricle. Upper panel: Ventral view of a 72 hpf embryo. Lower panel: Z-stack confocal images of the heart region from a 48 hpf embryo. A: atrium. AVC: atrioventricular canal. OFT: outflow track. V: ventricle. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Junction PCR and direct sequencing results of individual positive F1 progeny from outcrosses of each of the three positive founders (#3, #5 and #12). Due to an extra copy of the T5R1 primer sequence in the PoR-Ne donor, PCR with the primer pair T5F2 and T5R1 targeting the donor plasmid results in a larger fragment than that of the F1 progeny. F1: an F1 embryo from F0 #12. Donor: tbx5a PoR-Ne donor plasmid. WT: pooled genomic DNA of five wild-type embryos.