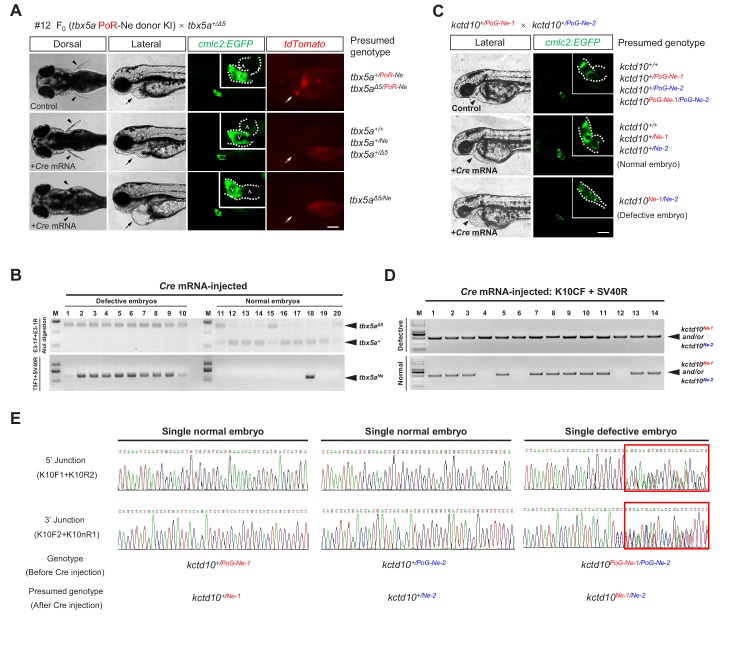
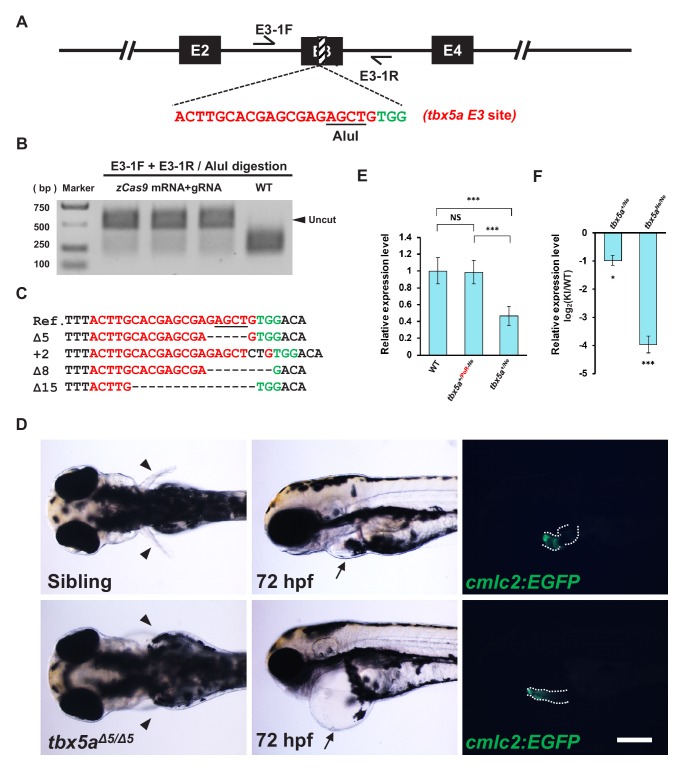
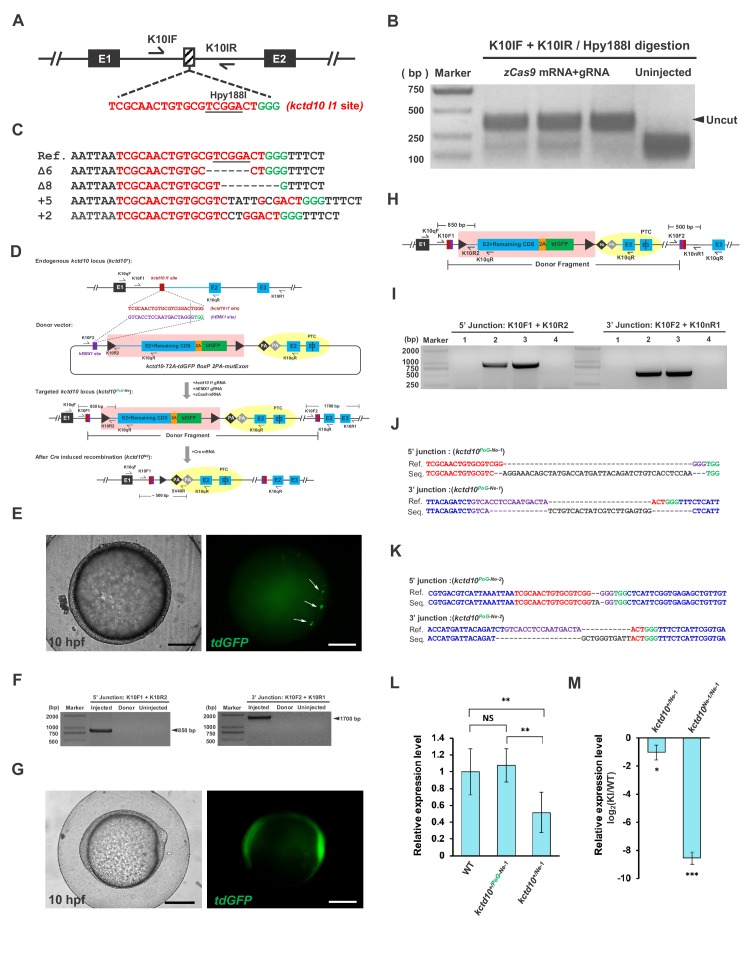
Figure 2. The tbx5a and kctd10 conditional alleles are responsive to Cre recombinase.
(A) Images of the 72 hpf progeny (F1) from a tbx5a+/Δ5 heterozygote crossed with the F0 #12 (mosaic for the tbx5aPoR-Ne allele) against the Tg(cmlc2:EGFP) transgenic background with or without Cre mRNA injection. The fluorescent images were obtained in the lateral view. Black arrowheads indicate pectoral fins, and black or white arrows indicate the heart. A: atrium. V: ventricle. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Genotyping results of the individual Cre mRNA-injected embryos obtained from the cross in A. (C) Images of the 48 hpf progeny (F2) derived from the cross of two kctd10 KI heterozygotes (F1), each carrying a different KI allele (kctd10PoG-Ne-1 from #32 and kctd10PoG-Ne-2 from #5) with the Tg(cmlc2:EGFP) transgenic background, to reveal the morphology of the heart. The white dotted line indicates the outline of the heart. The hearts in the upper and middle panels developed normally, showing obvious heart looping. In contrast, the heart in the lower panel shows defective development, exhibiting AVC malformations and heart looping failure. Black arrowheads indicate the heart. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) Genotyping by PCR amplification of the region flanking the loxP recombination site of the Cre mRNA-injected individual embryos obtained from the cross in C. (E) Representative junction PCR and direct sequencing results of the Cre mRNA-injected individual embryos showing normal or defective heart development obtained from the cross in C. As expected, the results indicate that the embryo showing the heart phenotype (labeled as ‘Single defective embryo’ in the figure) was a kctd10PoG-Ne-1/PoG-Ne-2 compound heterozygote (F2) before Cre mRNA injection since it showed overlapping peaks (red boxed region) in the sequencing results of the PCR products at both the 5’ and 3’ junctions (right panel), as the two alleles have different indel sequences at the junction sites. In contrast, the normal embryos (labeled as ‘Single normal embryos’ in the figure) were either kctd10+/PoG-Ne-1 or kctd10+/PoG-Ne-2 heterozygotes before Cre mRNA injection and therefore displayed uniform sequencing results corresponding to either the kctd10PoG-Ne-1 (or kctd10Ne-1) or kctd10PoG-Ne-2 (or kctd10Ne-2) allele, respectively. The expected corresponding sequences can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 2J and K.