Figure 2.
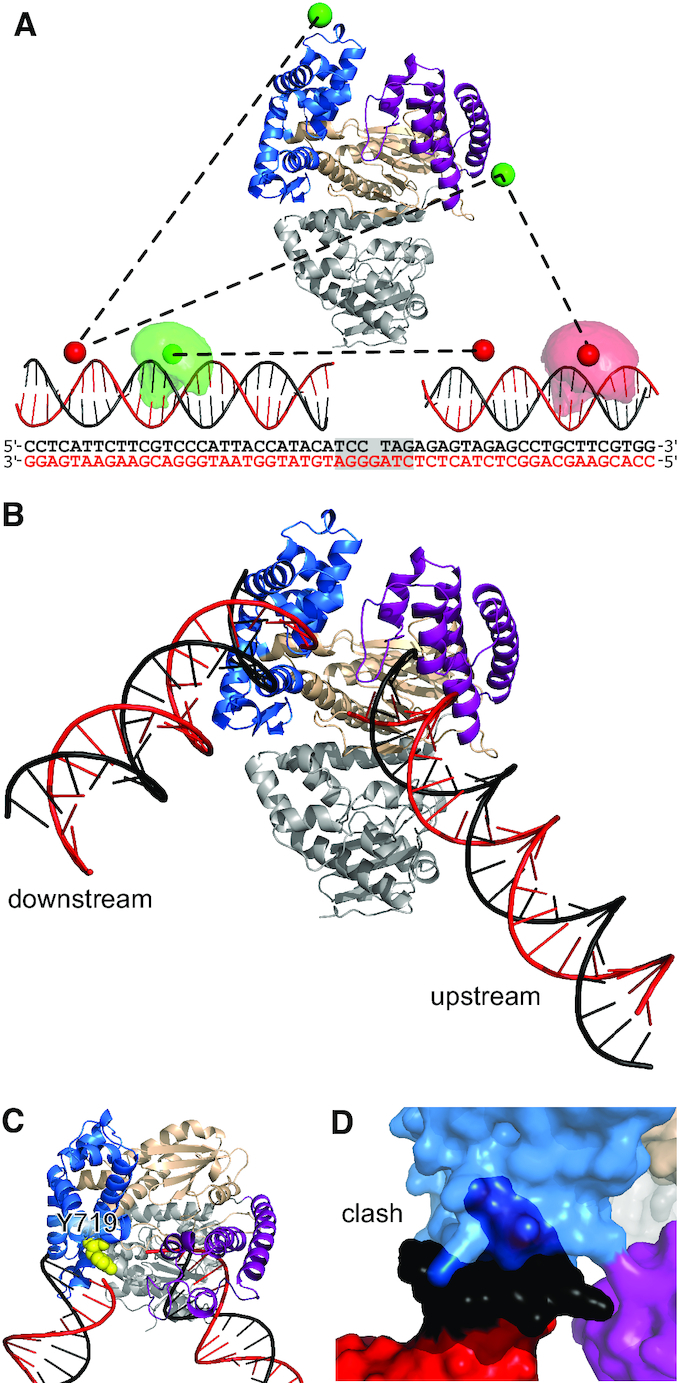
Pol-DNA binary structure from rigid-body docking. (A) Pol structure showing the fingers (blue), thumb (purple) and palm (wheat) subdomains and the proof-reading exonuclease domain (grey). Example DNA–DNA and protein DNA-distances (black dashed lines) are shown between mean dye positions (green and red spheres). Example accessible volumes of a donor (pale green cloud) and an acceptor (pale red cloud) dye are also shown, along with the full sequences of the docked DNAs; the shaded region indicating the DNA not used for the docking. (B) Results of the rigid-body docking: template DNA (red), non-template DNA (black), subdomains coloured as in (A). (C) Position of Y719 relative to downstream DNA. (D) Clash between full-length downstream DNA and the fingers subdomain (cyan). See also Supplementary Figure S2 and Supplementary Table S1.
