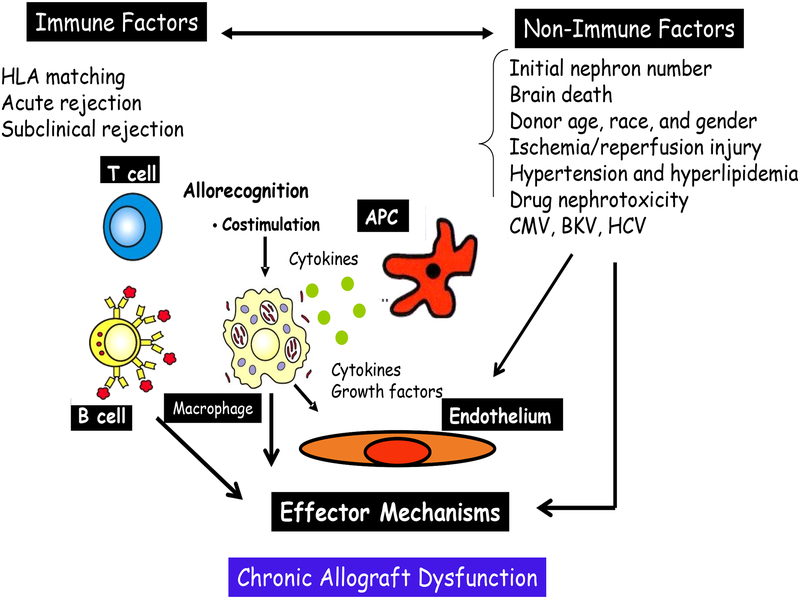
Figure 1:
The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these histopathological hallmarks remain obscure. Immunological and non-immunological factors have been associated with the progression to chronic allograft dysfunction. Many cell-cell, cell-matrix, and intracellular pathways have been implicated in the complex pathogenesis of CAN. CAN is characterized by slowly progressive graft dysfunction ultimately leading to chronic renal failure.