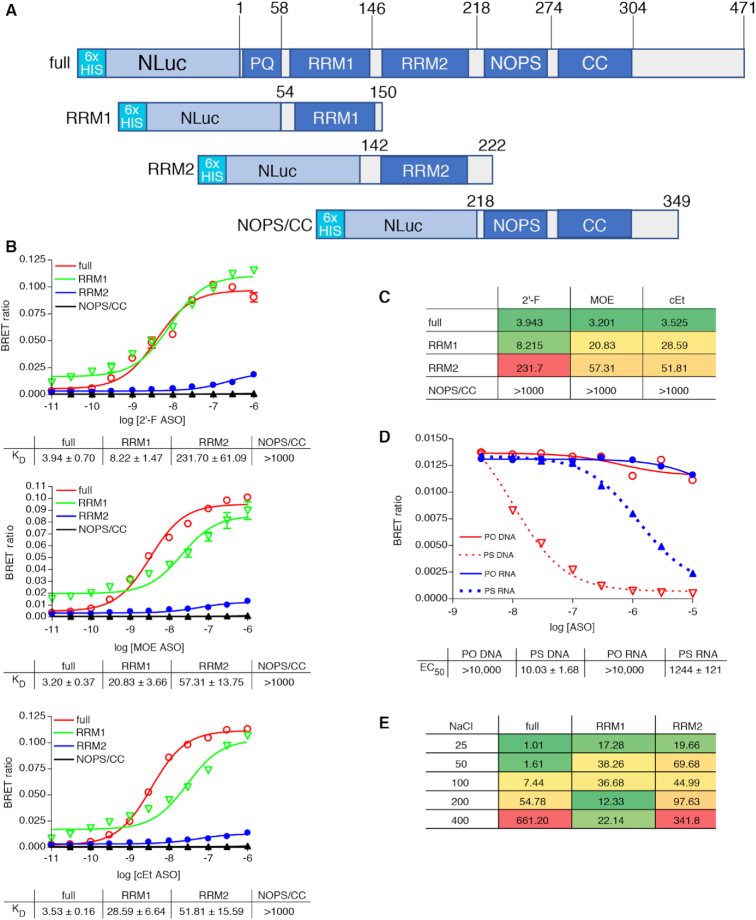
Figure 1.
(A) NLuc-P54nrb fusion constructs. NLuc was fused in frame to the amino-terminus of the P54 cDNA. RNA binding motifs RRM1 and RRM2, and core domain were cloned separately beginning and ending at the indicated amino acid positions. Expression of the fusion protein was confirmed by Western blot (Supplementary Figure S2A). (B) PS-ASOs bind P54nrb primarily via the RRM1 and RRM2 domains in a chemistry dependent manner. NLuc-P54nrb fusion proteins were immunopurified as detailed in Online Methods and subsequently incubated with Alexa 594 conjugated 5-10-5 2′-F, cEt, or MOE gap-mer PS-ASO at concentrations ranging from 10 pM to 1 μM. BRET ratios were determined for full-length P54nrb-NLuc (red), RRM1 (green), RRM2 (blue), or NOPS/coiled-coil (black). Concentration response curves and KD’s ± SEM (nM) are representative of two to three independent experiments. Data normalized to maximum BRET signal may be found in Supplementary Figure S2B. (C) KD’s (nM) are shown in tabular form with green = highest affinity; red = lowest affinity. (D) Competitive binding of PS and PO RNA and DNA ASOs to P54nrb. Unconjugated competing ASOs at 3–10 000 nM were combined with 10 nM Alexa-linked cEt gapmer PS-ASO 766636, then binding to p54nrb evaluated by NanoBRET. (E) Salt dependence of PS-ASO binding to P54nrb domains. KD’s (nM) for binding of cEt gap-mer ASO to p54nrb in 25–400 mM NaCl. Concentration response curves can be found in Supplementary Figure S4.