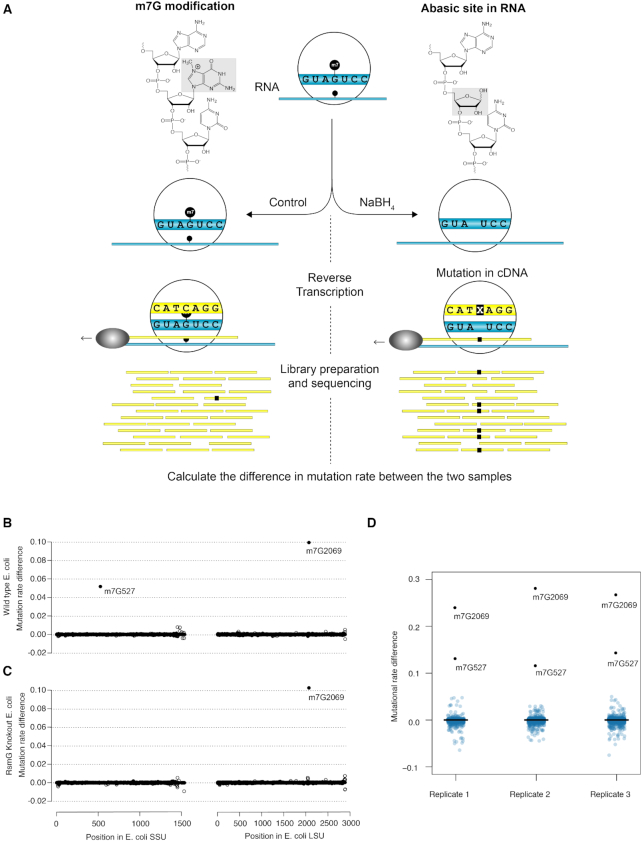
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the m7G-MaP-Seq method. NaBH4 treatment leads to formation of abasic sites at m7G positions, which subsequently are converted into cDNA mutations during reverse transcription and detecte by massive parallel sequencing. (B) Detection of m7G at E. coli SSU rRNA position 527 and E. coli LSU rRNA position 2069 in WT strain. (C) Detection of m7G at E. coli SSU rRNA position 527 and E. coli LSU rRNA position 2069 in RsmG knockout strain. (D) Boxplots showing consistent detection of m7G modified positions in biological replicates.