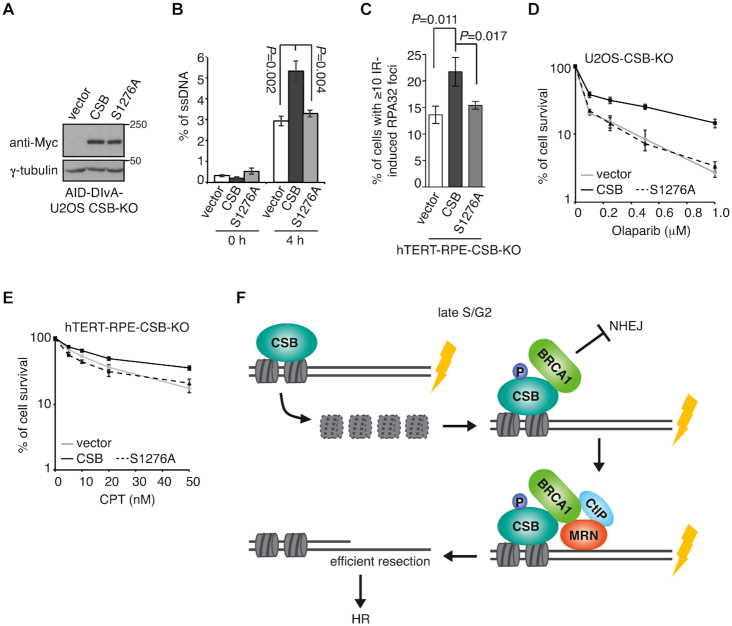
Figure 8.
CSB phosphorylation on S1276 promotes efficient DNA end resection and cell survival in response to DNA damage. (A) Western analysis of AID-DIvA-U2OS CSB-KO cells expressing various Myc-CSB alleles as indicated. (B) Quantification of the amount of ssDNA. AID-DIvA-U2OS CSB-KO cells stably expressing various indicated Myc-CSB alleles were treated with no 4-OHT or 4-OHT for 4 h. The amount of ssDNA generated at position 335 nt from AsiSI-induced DSB1 was measured as described in ‘Methods’. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated. (C) Quantification of cells with ≥ 10 IR-induced RPA32 foci. hTERT-RPE-CSB-KO cells expressing various Myc-CSB alleles as indicated were treated with 10 Gy IR and fixed 1 h later. Standard deviations from three independent experiments are indicated in this and subsequent panels. (D) Clonogenic survival assays of U2OS CSB-KO cells stably expressing various Myc-CSB alleles as indicated. (E) Clonogenic survival assays of hTERT-RPE-CSB-KO cells stably expressing various Myc-CSB alleles as indicated. (F) Model for the role of the CSB–BRCA1 interaction in promoting MRN- and CtIP-mediated DNA end resection. See the text for details.