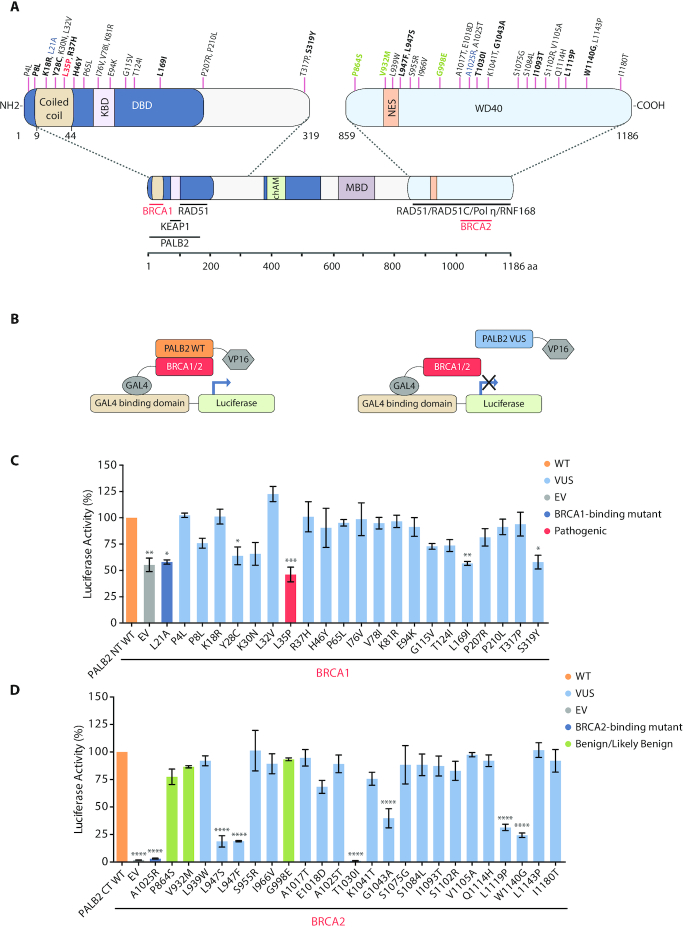
Figure 2.
Impact of PALB2 variants on BRCA1 and BRCA2 interaction by mammalian two-hybrid assay. (A) Schematic representation of the PALB2 protein and its domains along with the position of the N- and C-terminal missense variants selected in this study. Negative controls for BRCA1 and BRCA2 binding are in blue and the final prioritized variants in bold, with the p.L35P pathogenic variant highlighted in red and the benign/likely benign variants (as assigned by ClinVar) in green. PALB2 N- (aa 1–319) and C-terminal (aa 859–1186) interactors are also represented. KBD, KEAP1-binding domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; NES, nuclear export signal; MBD, MRG15-binding domain. (B) Mammalian two-hybrid assay representation. (C) BRCA1 (aa 1315–1863) and (D) BRCA2 (aa 1–60) interaction data; HEK293FT cells were co-transfected with BRCA1/2 and PALB2 N/C-terminal constructs and the reporter assay was performed 24 h post-transfection. Statistical significance was accessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc analysis (mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (*) P< 0.05; (**) P< 0.01; (***) P< 0.001 and (****) P< 0.0001.