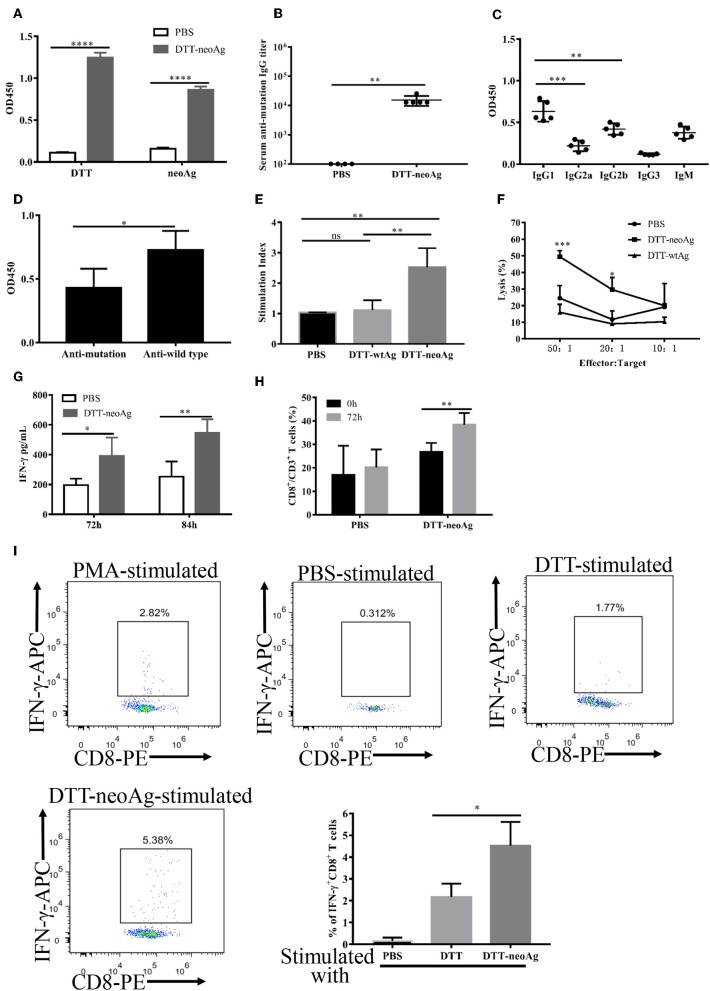
Figure 5.
Antibody responses and cellular immune responses elicited by DTT-neoAg vaccination in tumor challenged mice. The statistical significance was determined by Student's T-test. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. (A–D) C57BL/6 mice (n = 6–13) were administered s.c. with 2.5 × 104 B16 F10 cells into the right flank of the mice. Seven days after tumor challenge, mice were immunized three times at weekly intervals with DTT-neoAg, DTT-wtAg, or PBS, formulated with Alum + CpG. (A) The mouse sera were collected on day 7 after the third immunization. The antibody responses were measured by ELISA with the sera 1:100 diluted and with the indicated coating antigens. (B) The anti-neoAg antibody titers were measured by ELISA. (C) Analysis of anti-neoAg antibody subclasses. (D) Anti-sera from DTT-wtAg-treated mice crossreact with neoAg. The sera were collected from mice immunized with DTT-wtAg after the third immunization, and the antibody specificity was analyzed by ELISA with sera 1:100 diluted and CTB-wtAg or CTB-neoAg as a coating antigen. (E) The splenocytes from indicated mice were stimulated in vitro with CTB-neoAg for 3 days. The stimulation indices was measured by CCK8 assay. (F) The cytotoxic T lymphocytes induced by DTT-neoAg vaccination. The splenocytes from DTT-neoAg-treated, or DTT-wtAg-treated, or PBS-treated mice were stimulated with CTB-neoAg for 3 days, and used as effector cells. B16F10 cells were used as target cells. The splenocytes and B16F10 cells were co-cultured at indicated ratios for 4 h at 37°C. The percentage of cell lysis was measured by LDH assay. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between DTT-neoAg-treated and DTT-wtAg-treated mice. (G) INF-γ production by in vitro neoAg-stimulated splenocytes of DTT-neoAg vaccinated mice. The splenocytes were stimulated with CTB-neoAg for 72 or 84 h, and the INF-γ in the culture supernatant was analyzed using a mouse IFN-γ ELISA kit. (H) CD8+ memory T cells induced by DTT-neoAg vaccination. The splenocytes of the vaccinated mice were in vitro stimulated with CTB-neoAg for 72 h, stained with anti-CD3ε-FITC anti-CD8-PerCP-Cy5.5, and the percentage of CD8+ T cells in CD3+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. (I) The splenocytes of DTT-neoAg-treated mice were incubated with antigen-loaded DC for 48 h, then Golgi-stop was added; 6 h later, the cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD3ε-PerCP-Cy5.5, anti-CD4- FITC, anti-CD8-PE Ab. After permeabilization, intracellular cytokines were stained with anti-IFN-γ-APC antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry.