Figure 1.
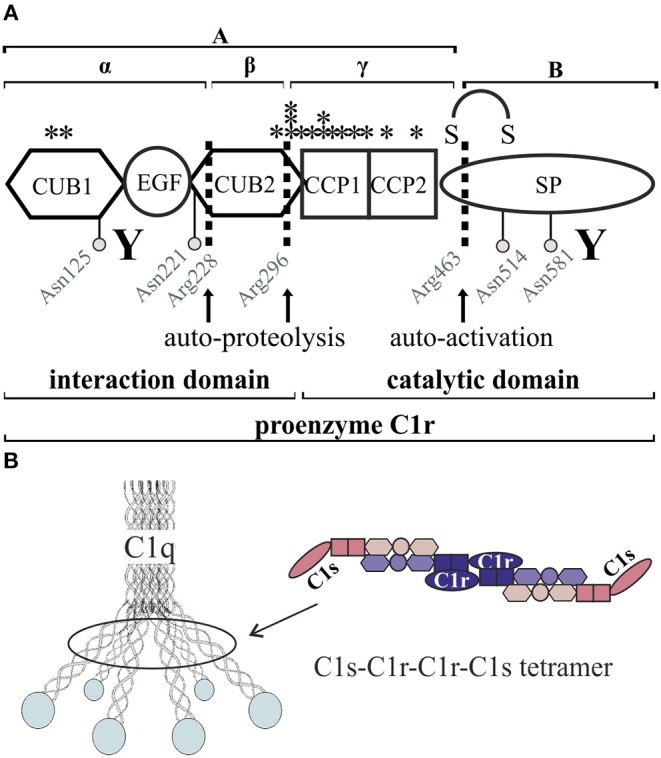
Schematic overview of C1r domain structure and secretion pattern. (A) Cleavage sites (arrows) as well as glycosylation sites (gray circles) are marked. Investigated pEDS variants (see also Table 2) are marked with stars. CUB1-EGF-CUB2 is described as the interaction domain and CCP1-CCP2-SP as the catalytic domain of C1r. “Y” indicates N- and C-terminal antibody target regions used in this study. Full-length proenzyme C1r has a molecular mass of ~100 kDa on western blot. Activation occurs through cleavage at Arg463, which produces the disulfide-linked A- and B-chains with apparent molecular masses when analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions of 55 and 38 kDa. C1r is also known to undergo two additional auto-proteolytic cleavages at Arg 228 and 296 in the A-chain that produce an N-terminal α-fragment with an apparent mass of 35 kDa, a β-fragment, and a γ-fragment disulfide-linked to the B-chain (5, 6). The fragments β and γ cannot be detected under reducing conditions by the C1r antibodies used in this study. (B) The C1 complex consists of a C1r2-C1s2 tetramer embedded into the umbrella-like hexamer of C1q heterotrimers.
