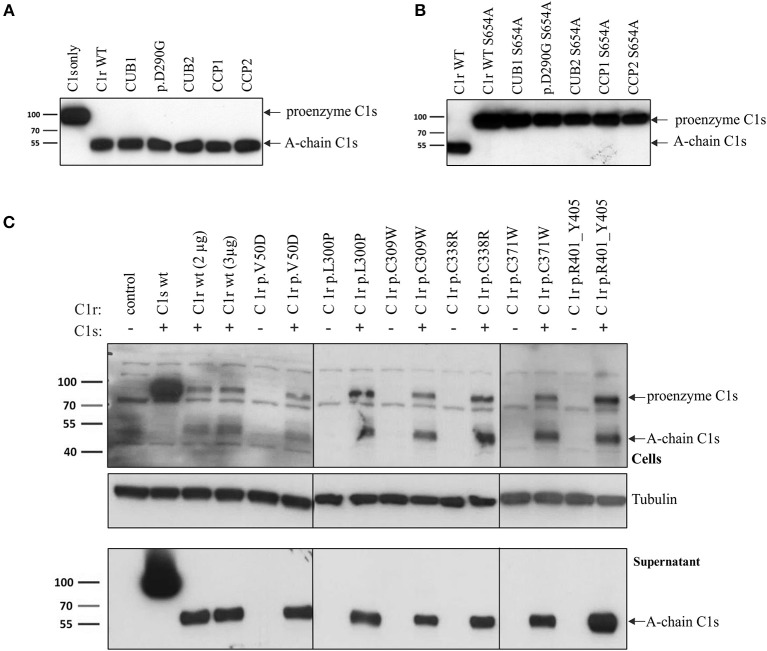
Figure 5.
All pEDS C1r variants retain enzymatic function toward C1s. Similarly to C1r, cleavage of proenzyme C1s (90 kDa) produces two disulfide-linked fragments: the C1s A-chain (N-terminal, 55 kDa) and B-chain (C-terminal). Presence of full-length C1s and cleaved C1s (A chain) was studied with an N-terminal anti-C1s antibody under reducing conditions. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with either C1r (WT or mutated) or C1s (WT), and supernatant was collected 48 h post-transfection. C1s supernatant was mixed 1:1 with supernatant from the different C1r overexpressing cells (C1r WT, CUB1, p.(D290G), CUB2, CCP1, CCP2; variants as in Figure 4), incubated for 1 h at 37°C, and used for western blot analysis. C1s cleavage was observed for all cell supernatant mixtures. (B) Repeating the analysis after introduction of the inactivating mutation p.S654A into the C1r constructs prevents enzymatic cleavage of C1s in all cases. (C) C1r (WT and different variants) was overexpressed either on its own or by co-transfection with C1s WT; C1s in cell lysate (upper panel) or supernatant (lower panel) was visualized by western blot. The results show that all C1r constructs remain activity toward C1s, and that C1r-mediated C1s cleavage already occurs within the cells.