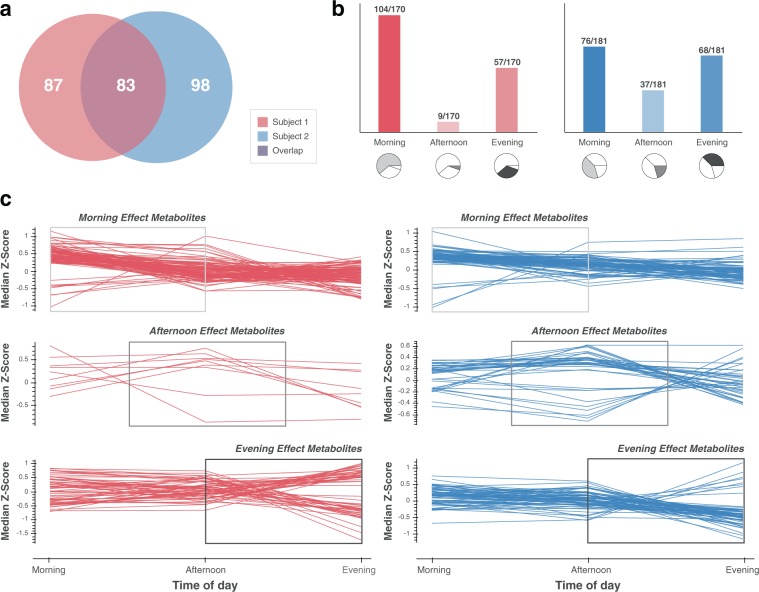
Fig. 4.
Daily metabolite fluctuations can be shared, distinct, or subject specific. a A subset of metabolite features for Subject 1 (n = 170) and Subject 2 (n = 181) were significantly (p < 0.05) affected by time of the day based on linear regression analysis (see Methods section). b While 83 metabolites were affected by time of the day for both Subjects, 87 and 98 were uniquely affected for Subject 1 and Subject 2, respectively. The majority of metabolites for Subject 1 had the greatest deviation from baseline in the morning, whereas metabolite deviations were more evenly distributed across the day for Subject 2. c Median Z-scores of metabolite concentrations throughout the course of the day. Metabolites with the greatest deviations in the morning appear to stabilize by evening (top row), while metabolites with an evening effect (bottom row) are close to baseline concentrations before spiking up or down in the evening. Metabolites with greatest deviations in the afternoon (middle row) peak in the afternoon and tend to reverse course by evening