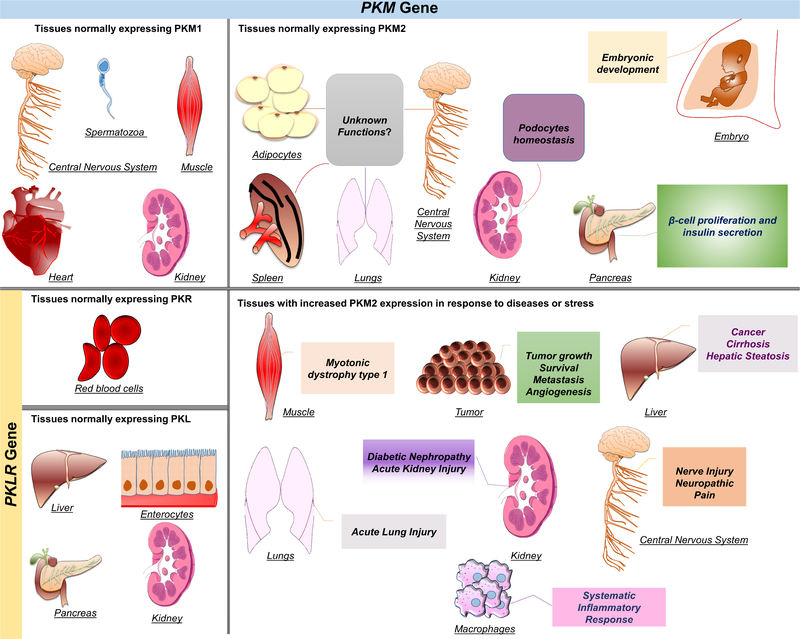
Figure 1. Tissue distribution of PK isoforms and the role of PKM2 in health and disease.
Mammalian pyruvate kinase has four isoforms transcribed by two different genes. PKL and PKR are both products of the PKLR gene, while PKM1 and PKM2 are products of the PKM gene. PKL is predominantly expressed in the liver and at lower levels in the pancreas, kidneys, and enterocytes. PKR is expressed in erythrocytes only. PKM1 is known to be expressed in muscle, mature spermatozoa, central nervous system, heart, and kidneys. PKM2 is the predominant isoform expressed during embryogenesis. It is also expressed in proliferative cells, and several healthy differentiated tissues, including pancreatic islets, adipose tissue, brain, kidneys, lungs, and spleen. However, the precise function of PKM2 in these tissues is largely unexplored. In addition, PKM2 is expressed in most tumors and within the liver under abnormal conditions such as cirrhosis, and hepatic steatosis. In activated macrophages, PKM2 expression is upregulated and contributes to sepsis and other inflammatory disorders. In tumors, PKM2 expression enhances aerobic glycolysis that provides cancer cells with growth advantages and has been associated with poor clinical outcomes.