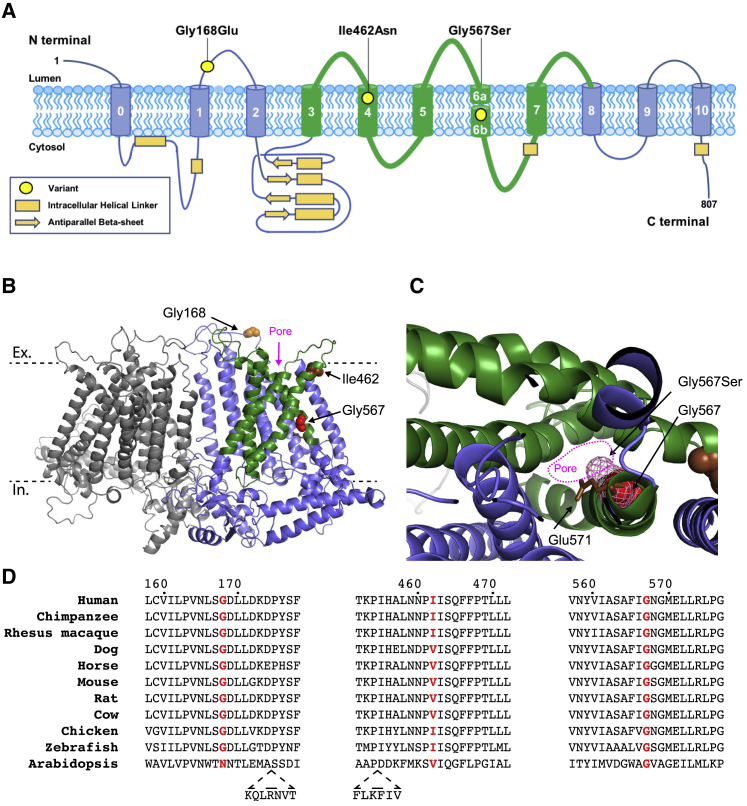
Figure 3.
Protein Structure and Variant Conservation
(A) Location of the three identified variants shown on a schematic representation of TMEM63A protein (Uniprot: O94886).
(B and C) Predicted structure TMEM63A protein based on cryo-EM structure of Arabidopsis homolog OSCA1.2 (PDB: 6MGV). The model was generated using SWISS-MODEL.21, 22 Residues altered by the variants are shown as spheres. The approximate location of the extracellular (Ex) and intracellular (In) surfaces of plasma membrane are indicated by dashed black lines. The five pore lining transmembrane helices are shown in green.21
(C) Section of TMEM63A structural model looking through pore region toward the extracellular domain. The Gly576 residue is shown as red spheres, and pink mesh indicates the predicted position the serine side-chain would occupy in the p.Gly576Ser mutant protein. The conserved residue, Glu571 (shown as brown sticks), that has been shown to reduce stretch activated ion conductance when mutated to alanine in OSCA1.2 can be seen adjacent to Gly576.21
(D) Clustal alignment of TMEM63A protein from ten vertebrate species and the Arabidopsis homolog OSCA1.2. The residues altered in the presented individuals are highlighted in red.