Figure 3.
Phenotypic Prototypes and Predictions from Naive Bayes Models
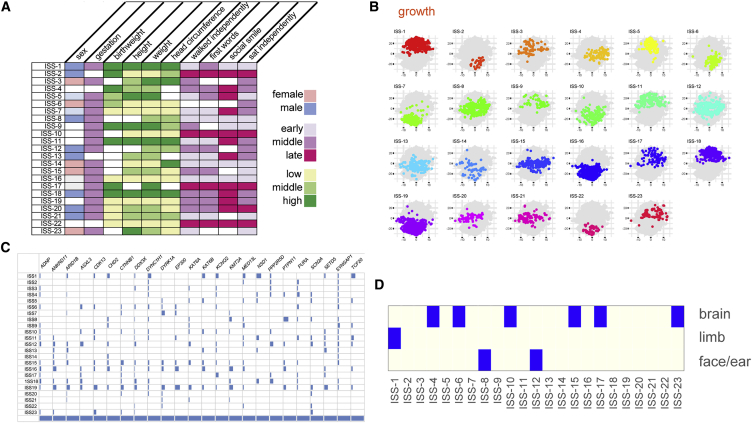
Unsupervised naive Bayes clustering of the 6,993 DDD probands into 23 distinct classes, here termed in silico syndromes (ISSBayes).
(A) A graphical representation of the phenotypic characteristics that define each ISSBayes using 10 discretized phenotypic values, a key is provided for each of the color-coded groups.
(B) Scatterplots show the projection into two dimensions by t-SNE of growth for each ISSBayes where symbols are color coded by ISS.
(C) To determine whether the ISSBayes showed any agreement with DNM in 24 different genes, we created a confusion matrix which did not indicate strong evidence of concordance of the phenotypic and genetic assignments.
(D) We also defined eight sets of HPO terms that describe site-specific malformations looked for over-representation of probands when categorized by profile (Fisher’s exact test). Three malformation types were enriched in nine different profiles (p value adjusted for testing 23 profiles, adjusted p ≤ 0.05 considered significant).