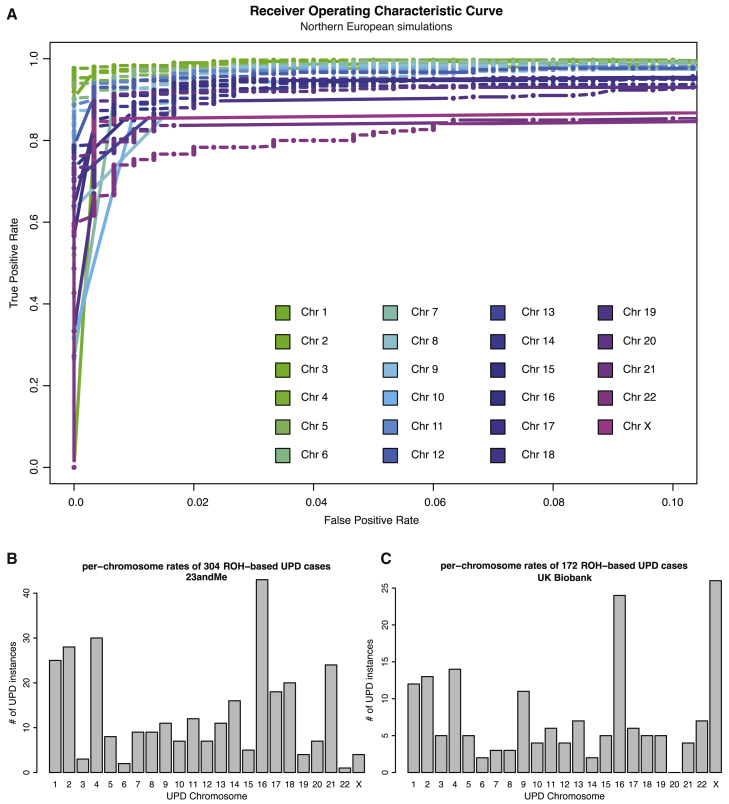
Figure 3.
Using ROH-Based UPD Detection, We Identified 304 UPD Case Subjects across Five Cohorts in the 23andMe Dataset and 172 UPD Case Subjects in the UK Biobank
We developed a per-chromosome simulation-based classification framework to search for putative UPD case subjects using ROH across five cohorts (northern European, southern European, Latino, African American, and East Asian individuals) in the 23andMe and in northern Europeans in the UK Biobank.
(A) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves show the performance of our per-chromosome UPD classifiers on simulated testing data, based on genotype data from northern Europeans in the 23andMe dataset. Our classifiers identified UPD with high accuracy (area under the ROC curve [auROC] > 0.9; TPR between 0.75 and 0.98 when FPR is fixed at 0.01). At fixed FPR, power is inversely related to chromosome length.
(B) The chromosome distribution of the ROH-based cases found in the 23andMe dataset recapitulates features of the chromosome distribution of true positives for UPD, which are identified through IBD analysis (Figure 2; Pearson’s correlation = 0.67; p value = 0.0005).
(C) The chromosome distribution of the ROH-based cases found in the UK Biobank also recapitulates features of the chromosome distribution of true positives for UPD identified through IBD analysis (Figure 2; Pearson’s correlation = 0.74; p value = 4.79 × 10−5). We note that parent-of-origin cannot be identified for ROH-based cases.