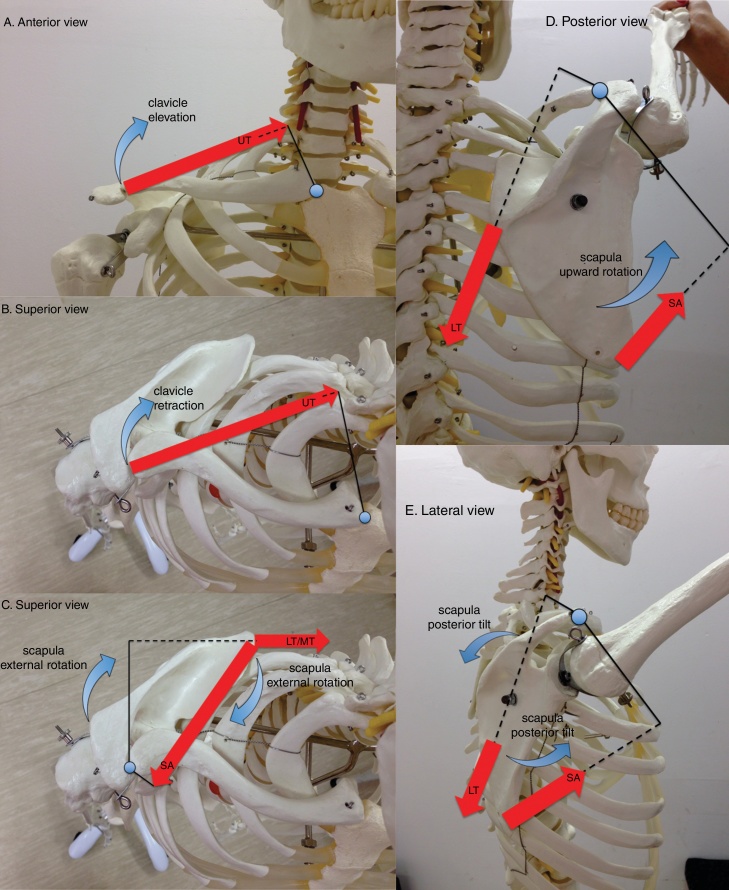
Figure 2.
Lines of action of selected scapulothoracic muscles are depicted by red large straight arrows (UT: upper trapezius, MT: middle trapezius, LT: lower trapezius, SA: serratus anterior). The muscles are shown contributing to clavicular elevation (A), clavicular retraction (B), scapular external rotation (C), scapular upward rotation (D), and scapular posterior tilt (E) during shoulder flexion. Internal moment arms for muscles are shown as a solid line from the axis of rotation to the line of action of each muscle. Dashed lines indicate a right-angle intersection between muscle's line of action and its moment arm. Note two axes of rotation: the sternoclavicular axis, located near the manubrium, and the acromioclavicular axis, located near the acromion.