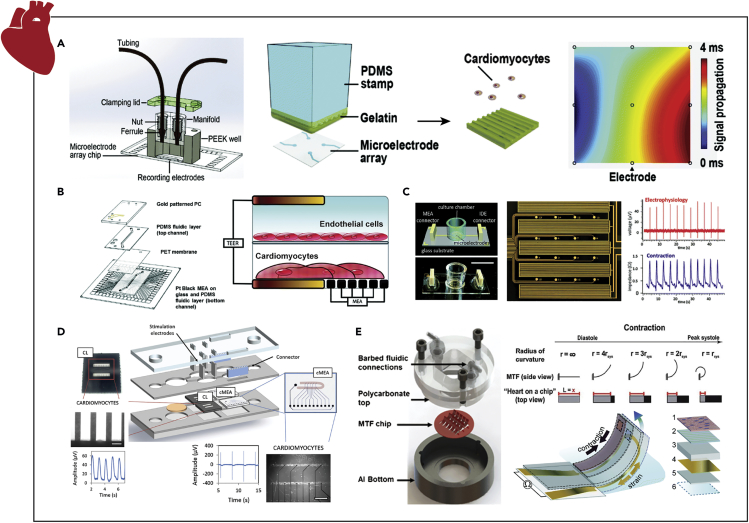
Figure 4.
Examples of Instrumented Organ-on-chip Models of the Heart
(A) Extracellular recordings of micropatterned stem-cell-derived CMs to study cardiac beating, field potentials, and conduction velocity via an MEA under vascular-like perfusion.
(B) Extracellular field potential duration and beat rate measurements from a CM/endothelial cell bilayer coculture model to assess the pharmacodynamics of altered vascular permeability via an MEA.
(C) Concurrent assessment of cardiac electrophysiology, beat rate, contractility, and viability via an MEA and IDEs with interpenetrating geometries for measuring field potentials and impedance, respectively.
(D) Parallel quantification of cardiac contraction force and electrophysiology of patterned stem-cell-derived CMs via independent cantilever system and MEA, respectively.
(E) Real-time cardiac tissue force quantification via the change in resistance caused by the deformation of piezoelectric MTF chips.
Reprinted and adapted with permission from: A (Kujala et al., 2016); B (Maoz et al., 2017); C (Qian et al., 2017); D (Oleaga et al., 2019); and E (Agarwal et al., 2013, Grosberg et al., 2011, Lind et al., 2017). CMs, cardiomyocytes; MEA, multielectrode array; IDEs, interdigitated electrodes; MTF, muscle thin films.