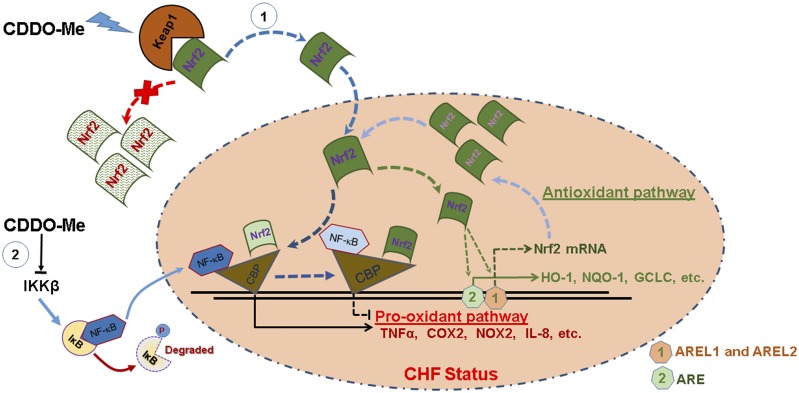
Fig. 8.
A schematic diagram of the potential mechanisms for CDDO-Me–mediated Nrf2 activation in CHF. On the one hand, CDDO-Me promotes the dissociation of Nrf2 from Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1; a natural Nrf2 inhibitor) in the cytosol, thus translocating to the nucleus where enhanced binding of Nrf2 to CBP promotes pro-antioxidant pathways, and reduced binding of NF-κB to CBP results in the inhibition of the pro-oxidant pathway in CHF. At the same time, Nrf2 binds to its own promoter at AREL1 and AREL2 sites to amplify its antioxidative effects by increasing its own transcription. On the other hand, CDDO-Me may inhibit the binding of NF-κB to DNA and subsequent transcriptional activation through the direct interaction with IκB kinase (IKK) β to prevent NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation. AREL1 and AREL2, Antioxidant Response Element (ARE)-Like Sequence 1 and 2.