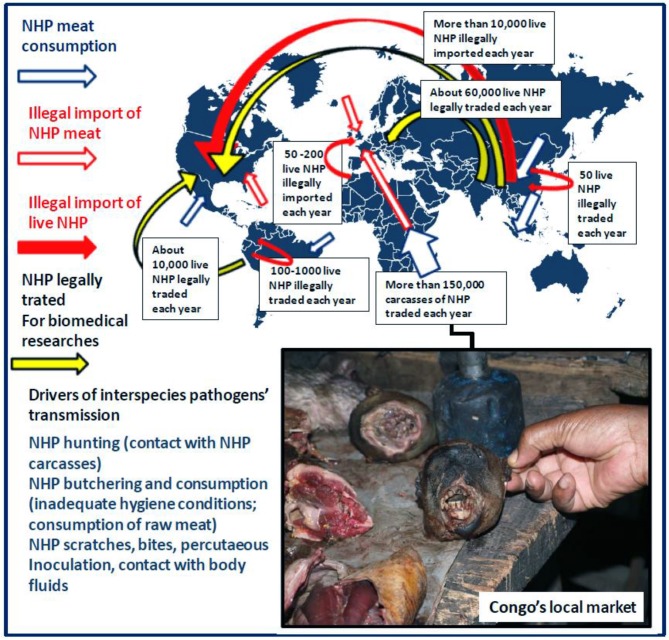
Figure 1.
Drivers of interspecies pathogen transmission from NHP to humans including incidents with NHP (in wildlife ecosystem or after illegal import of live NHP), contact with NHP carcasses, NHP consumption (local consumption and illegal import of NHP meat). According to the CITES database for 2005–2014, the global primate trade was estimated 450,000 NHP/year. The figure illustrates the dynamics of the annual legal trade and illegal traffic of live NHP at the international level as well as the local trade and consumption of NHP carcasses according to Fa et al. (9), Van Lavieren (11), Smith et al. (12), and Nijman et al. (13). Obviously, it is almost impossible to draw an exhaustive view of the global primate trade and particularly of the NHP illegal trade as the information available is only based on reports of animal confiscations by customs or health services. Information on NHP meat consumption in South America and Asia is not available. Box: NHP wild meat in Congo's local market is a cheap source of food (Picture credit: Oleg Mediannikov).