Table 1. Optimization of reaction conditions a .
| |||
| Entry | Ligand | Additive (mol%) | Yield b [%] |
| 1 | X-Phos | CuI (30%) | 41 |
| 2 | P(4-CF3C6H5)3 | CuI (30%) | 50 |
| 3 | P(C6F5)3 | CuI (30%) | 39 |
| 4 | C-Phos | CuI (30%) | 32 |
| 5 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuI (10%) | 5 |
| 6 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuI (50%) | 56 |
| 7 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuI (100%) | 72 |
| 8 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuI (200%) | 80 |
| 9 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuI (250%) | 80 |
| 10 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuBr·Me2S (200%) | 83 |
| 11 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuTc (200%) | 31 |
| 12 | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuOAc (200%) | 29 |
| 13 c | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuBr·Me2S (200%) | 85 |
| 14 c , d | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuBr·Me2S (200%) | 99 |
| 15 c , e | P(4-CF3C6H4)3 | CuBr·Me2S (200%) | 95 (92) f |
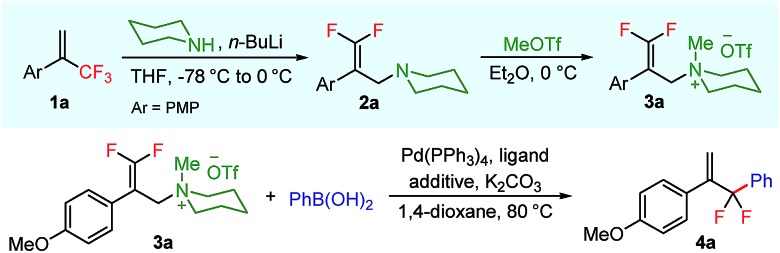
aReaction conditions (unless otherwise specified): 3a (0.1 mmol, 1.0 equiv.), PhB(OH)2 (2.0 equiv.), Pd(PPh3)4 (10 mol%), ligand (20 mol%), additive (30 mol%), K2CO3 (2.0 equiv.), 1,4-dioxane (1 mL), 80 °C, and 20 h.
bYields determined by 19F-NMR spectroscopy using trifluoromethylbenzene as an internal standard.
cCs2CO3 instead of K2CO3.
d5 Å molecular sieve (100 mg).
ePd(PPh3)4 (1 mol%) and P(4-CF3C6H4)3 (2 mol%).
fIsolated yield.
