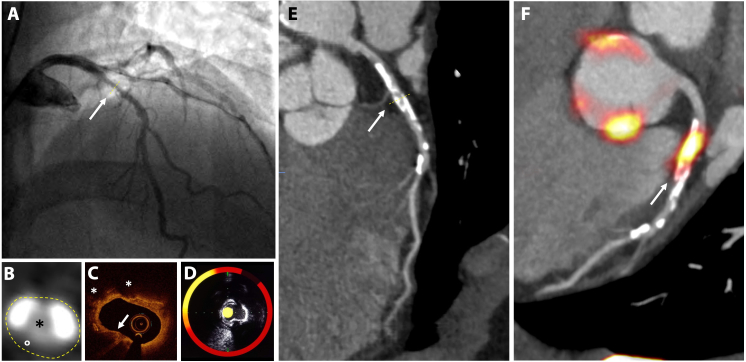
Figure 2.
Imaging of coronary atherosclerosis in a patient with non-ST elevated myocardial infarction. (A) Catheter angiography shows an irregular lesion in the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery (artery). (B) Transaxial view of the coronary lesion on CT (i) shows a complex plaque with calcified (white) and fibrofatty (°) plaque around a central lumen (*). (C) Optical coherence tomography detects a thin fibrous cap (arrow) and lipid pools (*). (D) Combined near infrared spectroscopy and intravascular ultrasound confirms high lipid burden within the plaque (yellow). (E) Centreline reconstruction of the left anterior descending artery visualizes calcification and plaque formation throughout the entire vessel. (F) 18F-Sodium fluoride positron emission tomography/ CT detects high uptake in the atherosclerotic plaque