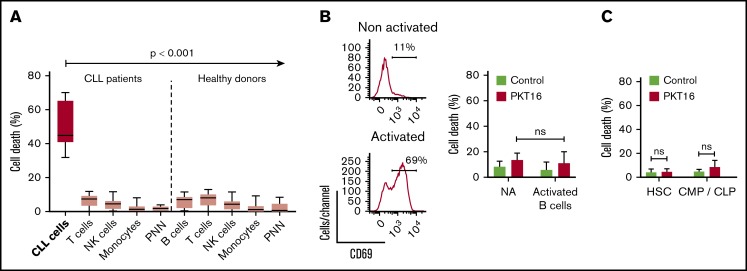
Figure 3.
PKT16 selectively targets the malignant CLL cells. (A, left) CLL B cells (n = 6), T-cells (n = 9), natural killer (NK) cells (n = 5), monocytes (n = 5), and polynuclear neutrophils (PNN; n = 9) were isolated from patients with CLL and incubated with PKT16 (100 µM, 6 hours), and the cytotoxicity induced was evaluated by Annexin-V/PI colabeling. The percentages of Annexin-V-positive cells were recorded and graphed. (Right) B cells (n = 9), T cells (n = 10), NK cells (n = 10), monocytes (n = 11), and PNNs (n = 8) were isolated from healthy donors, treated with PKT16 (100 µM, 6 hours), and the PCD induced was assessed by flow cytometry as above. (B, left) Flow cytometry panels of CD69 staining performed on B cells before (not activated) and after activation with interleukin 4 (50 ng/mL) and CD40L (100 ng/mL; activated cells). Numbers indicate the percentages of CD69 positive cells. (Right) PCD was measured after PKT16 treatment (100 µM, 6 hours) by Annexin-V/PI colabeling in control (nonactivated; NA) and activated/gathered CD69-positive B cells. The percentages of Annexin-V-positive cells were recorded and expressed as a histogram (n = 6 donors). (C) Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC; n = 7) and common myeloid and lymphoid progenitors (CMP/CLP; n = 6) were purified from the bone marrow of healthy donors and incubated with PKT16 (100 µM, 6 hours). Cell death was assessed by Annexin-V/PI colabeling and the Annexin-V-positive cells were quantified and expressed as a percentage (n = 7 donors). Statistical significance was calculated by Mann-Whitney U test. Symbols and bars represent mean ± SD.