Figure 2.
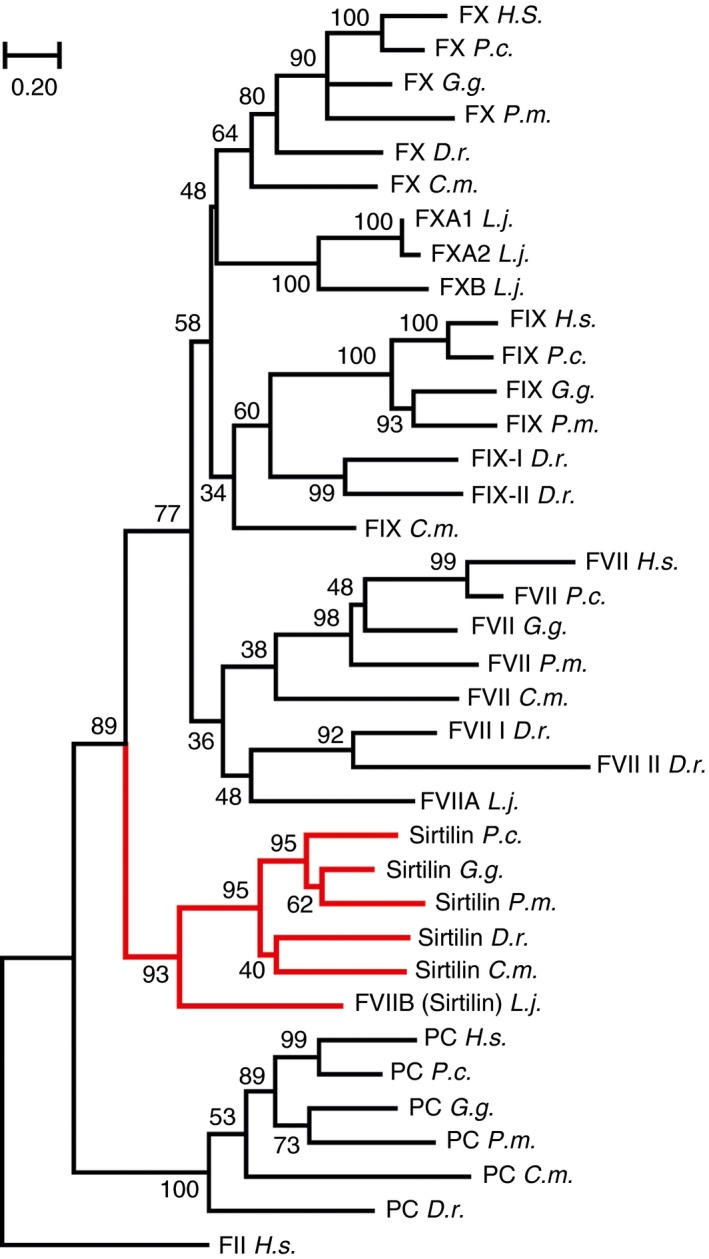
Phylogenetic analysis of sirtilins and related vitamin K‐dependent proteases. A neighbor‐joining tree of the highest log likelihood (− 12 192.26) is shown, with branch lengths representing the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The reliability of the branches is given at the nodes as a percentage of 1000 bootstrap replicates. Human prothrombin (FII) was used as the outgroup. Homologs of sirtilin are highlighted in red. Sequences of the catalytic domains of Homo sapiens (H.s.), Phascolarctos cinereus (P.c.), Gallus gallus (G.g.), Protobothrops mucrosquamatus (P.m.), Danio rerio (D.r.), Callorhinchus milii (C.m.) and Lethenteron japonicum (L.j.) were analyzed as shown in Table S1.
