Figure 1.
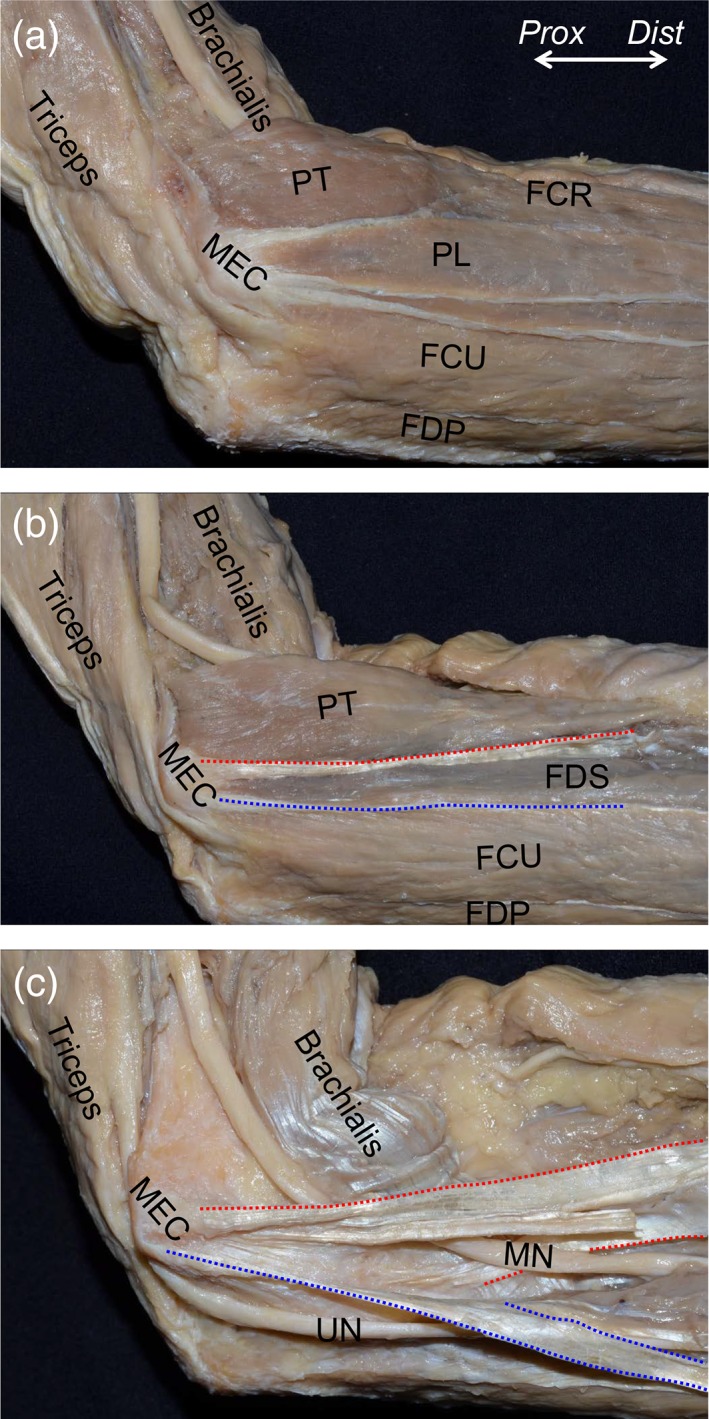
Muscular and tendinous structures of the flexor‐pronator muscles (FPMs). The medial aspect of the left elbow is shown. (A) After removal of the superficial fascia, FPMs were shown to form a common muscular origin on the medial supracondylar ridge and the medial epicondyle of the humerus (MEC). (B) The palmaris longus (PL) and flexor carpi radialis (FCR) muscles were removed, and the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) muscle was exposed. Between the pronator teres (PT) and FDS muscles (red dotted line), and the FDS and flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscles (blue dotted line), the tendinous septa (TS) could be identified. (C) After removal of muscular parts of the PT, FDS, and FCU muscles, the median nerve (MN) was shown to penetrate the TS between the PT and FDS muscles (red dotted area), and the ulnar nerve (UN) passed posterior to the TS between the FDS and FCU muscles (blue dotted area). FDP, flexor digitorum profundus; Dist, distal; Prox, proximal. [Color figure can be viewed at https://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
